前言
传统关系型数据库比如Mysql,正常情况下能支持几千左右的QPS。如果负载变高,就需要考虑缓存系统了,现在最常使用的缓存是Redis,QPS轻松到10+万。
Redis官网https://redis.io/docs/latest
架构图
Redis,REmote DIctionary Server,顾名思义就是远程的字典服务。
Redis单实例结构比较简单,多路IO复用 + 单线程读写内存大MAP + 即时刷磁盘。
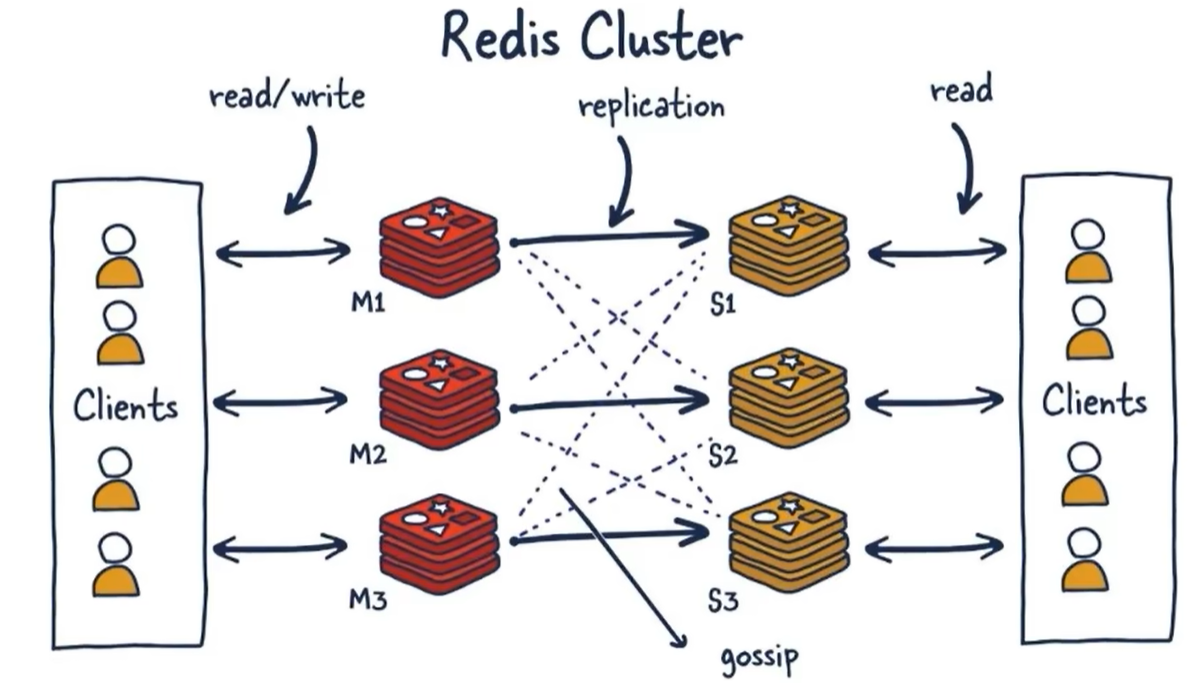
下面是Cluster模式下的架构图
数据类型与命令
Redis作为一个KV结构的缓存,Key和Value的定义如下
struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4;
unsigned encoding:4;
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
* and most significant 16 bits access time). */
int refcount;
void *ptr;
};
Value里面嵌套的类型则非常丰富。
- String
字符串的定义在文件src/sds.h,可以看到Redis对内存的使用是很精细的,不同长度的字符串还分别使用了不同的结构。/* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly. * However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings. */ struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 { unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */ char buf[]; }; struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 { uint8_t len; /* used */ uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */ unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */ char buf[]; }; struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 { uint16_t len; /* used */ uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */ unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */ char buf[]; }; struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 { uint32_t len; /* used */ uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */ unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */ char buf[]; }; struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 { uint64_t len; /* used */ uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */ unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */ char buf[]; }; - List
List是一个经典的双向列表src\adlist.h。typedef struct listNode { struct listNode *prev; struct listNode *next; void *value; } listNode; typedef struct listIter { listNode *next; int direction; } listIter; typedef struct list { listNode *head; listNode *tail; unsigned long len; } list; - Hash
一个字典类型Dict,内部实现为Hash Table。 -
Set
根据存储数据的性质不同,内部可以是intSet,压缩数组listpack或者Dict。
压缩数组就是元素长度不固定的数组,/* Each entry in the listpack is either a string or an integer. */ typedef struct { /* When string is used, it is provided with the length (slen). */ unsigned char *sval; uint32_t slen; /* When integer is used, 'sval' is NULL, and lval holds the value. */ long long lval; } listpackEntry; - Sorted Set
一般也称为ZSet,当数据量较小时使用压缩表listpack,否则使用跳跃表zskiplist和Dict。/* ZSETs use a specialized version of Skiplists */ typedef struct zskiplistNode { sds ele; double score; struct zskiplistNode *backward; struct zskiplistLevel { struct zskiplistNode *forward; unsigned long span; } level[]; } zskiplistNode; typedef struct zskiplist { struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail; unsigned long length; int level; } zskiplist; typedef struct zset { dict *dict; zskiplist *zsl; } zset;
Redis为了优化内存使用,是使用了很多奇技淫巧的。比如压缩列表(别的场合可能为了更快就采用一个固定大长度的数组了)和跳跃表(Java里有序字典就是Hash Table+链表的组合)。
Redis支持的所有命令都有对应的json说明文件src\commands\*.json,映射的函数都在这个文件src\server.h。
所有的命令文档在这里https://redis.io/docs/latest/commands
Hash Table
Redis的字典Dict的实现代码在dict.h。底层的HasTable结构复杂度为O(1),这也是Redis快的一个关键因素。
struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next; /* Next entry in the same hash bucket. */
};
struct dict {
dictType *type;
dictEntry **ht_table[2];
unsigned long ht_used[2];
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
/* Keep small vars at end for optimal (minimal) struct padding */
unsigned pauserehash : 15; /* If >0 rehashing is paused */
unsigned useStoredKeyApi : 1; /* See comment of storedHashFunction above */
signed char ht_size_exp[2]; /* exponent of size. (size = 1<<exp) */
int16_t pauseAutoResize; /* If >0 automatic resizing is disallowed (<0 indicates coding error) */
void *metadata[];
};
注意这里的ht_table有2份。Java库中的HashTable,是写时触发,先resort完毕,然后再调用put写入新数据。Redis因为内存很大,为了避免延迟,在后台线程中异步增量rehash。在rehash期间同时保持有新旧两张索引表。
增量rehash的代码在server.c,而且每1秒中最多只做1ms事,多了就等下个周期。
void databasesCron(void) {
/* Expire keys by random sampling. Not required for slaves
* as master will synthesize DELs for us. */
if (server.active_expire_enabled) {
if (iAmMaster()) {
activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW);
} else {
expireSlaveKeys();
}
}
/* Defrag keys gradually. */
activeDefragCycle();
/* Perform hash tables rehashing if needed, but only if there are no
* other processes saving the DB on disk. Otherwise rehashing is bad
* as will cause a lot of copy-on-write of memory pages. */
if (!hasActiveChildProcess()) {
/* We use global counters so if we stop the computation at a given
* DB we'll be able to start from the successive in the next
* cron loop iteration. */
static unsigned int resize_db = 0;
static unsigned int rehash_db = 0;
int dbs_per_call = CRON_DBS_PER_CALL;
int j;
/* Don't test more DBs than we have. */
if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum) dbs_per_call = server.dbnum;
for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call; j++) {
redisDb *db = &server.db[resize_db % server.dbnum];
kvstoreTryResizeDicts(db->keys, CRON_DICTS_PER_DB);
kvstoreTryResizeDicts(db->expires, CRON_DICTS_PER_DB);
resize_db++;
}
/* Rehash */
if (server.activerehashing) {
uint64_t elapsed_us = 0;
for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call; j++) {
redisDb *db = &server.db[rehash_db % server.dbnum];
elapsed_us += kvstoreIncrementallyRehash(db->keys, INCREMENTAL_REHASHING_THRESHOLD_US - elapsed_us);
if (elapsed_us >= INCREMENTAL_REHASHING_THRESHOLD_US)
break;
elapsed_us += kvstoreIncrementallyRehash(db->expires, INCREMENTAL_REHASHING_THRESHOLD_US - elapsed_us);
if (elapsed_us >= INCREMENTAL_REHASHING_THRESHOLD_US)
break;
rehash_db++;
}
}
}
}
持久化
- RDB(Redis Database)
通过save/bgsave命令持久化数据到rdb文件。bgsave是异步的(在fork的子进程中执行rdbSave),其他过程和save没有区别。内部就是遍历dict记录一条一条写入文件,达到持久化的目的。代码在src\rdb.c。
RDB是早期的持久化方案,有两个明显的缺陷:一个是fork写文件不够实时;一个是全量写文件可能导致请求卡顿。优点是:rdb文件基本是内存的镜像,所以加载速度很快。 -
AOF(Append Only File)
AOF和关系型数据库里的WAL机制基本类似。每个写命令在处理内存后都会通过feedAppendOnlyFile先写到缓冲区server.aof_buf,然后通过flushAppendOnlyFile写到AOF文件。
AOF写日志很及时,甚至可以做到实时写文件。但是因为是日志信息,所以加载时速度比RDB慢很多。
高可用
-
Master-Slave
主从模式只需要在从机上配置一下主机地址即可
slaveof <masterip> <masterport>
可以配置1主1从或者1主多从,可以在这个基础上实现读写分离。
主机故障,需要手动切换。 -
Sentinel
在主从模式的基础上,启动哨兵进程redis-sentinel来做监控,实现故障自动切换。
周期性的ping、info、hello动态维护节点状态。 -
Cluster
一种服务器Sharding技术,分片和路由逻辑都在服务端。每个分区内部还是主从模式,使用Gossip协议来实现去中心化的分布式。同时保证了高可用和扩展性。
安装
yum install redis
systemctl enable redis
systemctl start redis
Reids单实例就安装完毕了。
配置文件位置/etc/redis.conf,重要的几个参数
port 6379
dbfilename dump.rdb
dir /var/lib/redis
save 900 1 //RDB触发机制
save 300 10
save 60 10000
appendfsync everysec //每秒一次的AOF
先部署4个单机服务,然后在任意一个服务上使用命令来创建集群。
redis-cli --cluster create --cluster-replicas 1 1.1.1.1:8000 2.2.2.2:8000 3.3.3.3:8000 4.4.4.4:8000
这个命令会自动分配主备机,并且平均分配槽位。
槽位与扩容
在Cluster特性上线前,应用为了水平扩展,都是通过客户端一致性hash来实现,由客户端决定去哪个实例上读写数据。日常维护和故障恢复对运维的要求比较高。
Cluster是去中心化的,在服务端以槽位slot来分配数据存储。总槽数16384,分配槽位slot = crc16(key,keylen) & 0x3FFF。
以下是Cluster集群扩容步骤
- 通过cluster nodes命令查看当前集群节点状态和槽位分配关系
- 启动新Redis实例并加入集群cluster add-node
需要选择跟随的源节点 - 在需要扩容的主实例上重新分配槽位cluster reshard
需要选择分配多少个槽位,但是无法选择具体槽位。 - 新建Redis从实例并加入集群cluster add-node
缩容就是reshard和del-node配合,大同小异。
分布式锁
Redis的事务,严格来说其实只有原子性,还是在lua脚本的帮助下。持久化,隔离性,一致性这三个维度都很勉强。所以在做分布式锁的时候,需要Redisson这样的客户端做很多事情来保证尽可能的可靠。在强调一致性的场合,推荐使用Zookeeper的分布式锁,完全的强一致性。
下面是Redisson的加锁和解锁过程。
class RedissonLock
{
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
return evalWriteSyncedNoRetryAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if ((redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) " +
"or (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1)) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.singletonList(getRawName()), unit.toMillis(leaseTime), getLockName(threadId));
}
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId, String requestId, int timeout) {
return evalWriteSyncedNoRetryAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"local val = redis.call('get', KEYS[3]); " +
"if val ~= false then " +
"return tonumber(val);" +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
"if (counter > 0) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
"redis.call('set', KEYS[3], 0, 'px', ARGV[5]); " +
"return 0; " +
"else " +
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
"redis.call(ARGV[4], KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"redis.call('set', KEYS[3], 1, 'px', ARGV[5]); " +
"return 1; " +
"end; ",
Arrays.asList(getRawName(), getChannelName(), getUnlockLatchName(requestId)),
LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime,
getLockName(threadId), getSubscribeService().getPublishCommand(), timeout);
}
}
Gossip
Gossip的代码在cluster_legacy.h。
Gossip协议本身另开一篇文章详细讲。
微信扫描下方的二维码阅读本文

0 Comments