项目loom
Java协程的孵化项目loom在2017年就开始了。这是loom的项目目标。https://cr.openjdk.org/~rpressler/loom/Loom-Proposal.html
虚拟线程在Java19中第一次以预览版的形式对外开放,在Java21中正式成为语言的一部分。
https://openjdk.org/jeps/444
关键角色
- 应用实际任务Runnable
虚拟线程的服务目标,整个协程机制就是为了能透明的挂起和恢复他的执行。 - 协程Continuation
对Runnable的封装,以支持挂起和恢复。 - 调度器ForkJoinPool
这是一个work-stealing模式的调度器,负责调度协程。这里的工作线程就是协程的carrierThread。 - 阻塞点改造LockSupport.park&unpark
虚拟线程是有栈协程(Stackfull),能在任意阻塞点支持挂起。所以Java基础库的阻塞点都需要做一定程度的改造以支持Continuation的挂起和恢复。包括Object.wait、java.util.concurrent.locks、java.net.Socket等。 - 历史兼容VirtualThread
Java应用的历史代码绝大部分都是Thread+Runnable模式的,如果协程能够继承Thread的接口,对兼容历史代码有极大的好处。
虚拟线程在Java层的几个类关系如下
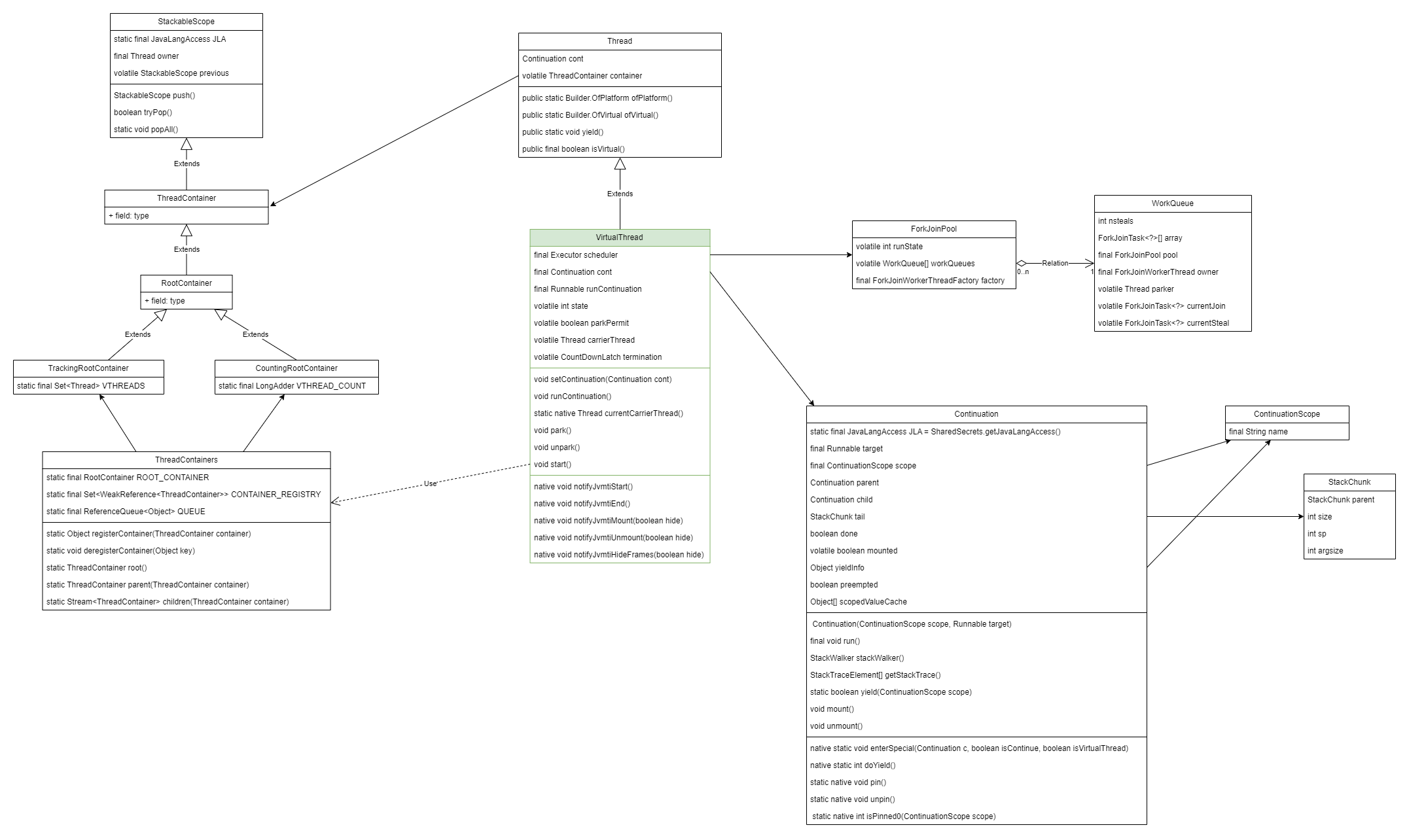
如何使用
因为VirtualThread已经考虑了兼容性,所以使用起来足够简单和方便。
- 代码中使用
以前创建线程的地方,现在创建虚拟线程来代替就可以了。Thread.ofVirtual().start(Runnable task)。如果是Web容器(tomcat之类的),只需要改一个配置就能切换过来,享受虚拟线程带来的好处。 - 配套支持
JVMTI、JFR、JDWP这些工具都是经过改造,支持虚拟线程的。 - 注意事项
暂时还不支持monitor和native状态下的切换。代码里有synchronized关键字的要谨慎使用协程,synchronized如果阻塞太久,会拖垮整个服务。synchronized关键字这个是有计划要解决的。
协程栈帧切换全景
之前的Java栈帧是套在机器栈帧里,现在协程的栈帧又套在Java栈帧里。栈帧切换起来有点复杂,代码参见hotspot\share\runtime\continuationFreezeThaw.cpp
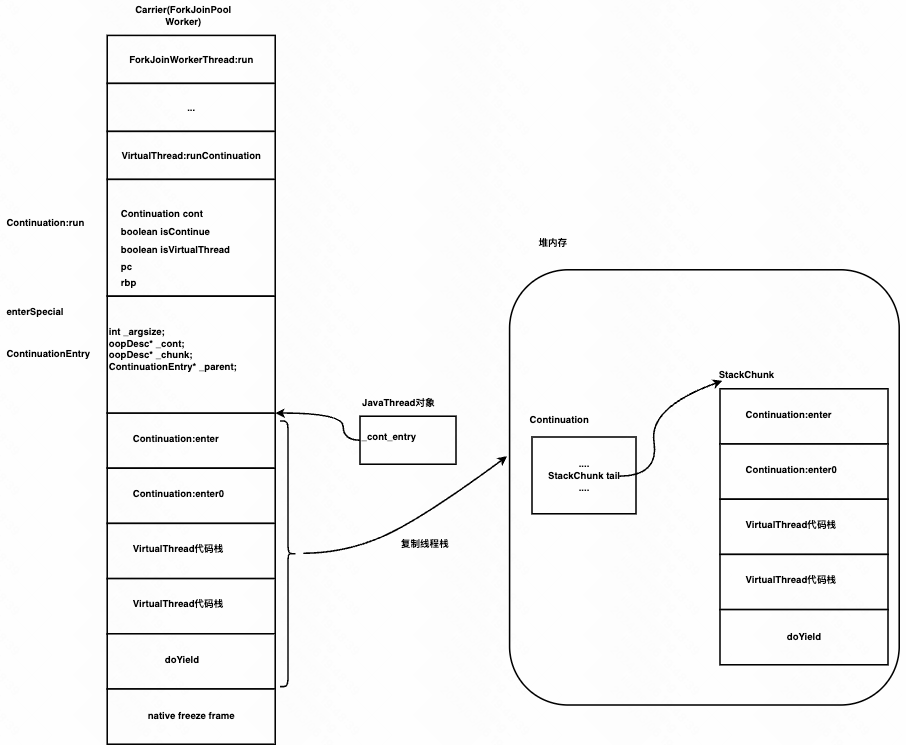
Java层流程
平台线程和虚拟线程之间的挂机&恢复等切换流程都在Java层控制,具体可以看src\java.base\share\classes\java\lang\VirtualThread.java
- 启动协程任务VirtualThread.start
重点在Continuation.runContinuation函数
public void start() {
start(ThreadContainers.root()); //线程跟踪RootContainer.TrackingRootContainer
}
private void start(ThreadContainer container) {
if (!compareAndSetState(NEW, STARTED)) {
throw new IllegalThreadStateException("Already started");
}
// bind thread to container
assert threadContainer() == null;
setThreadContainer(container); //Thread.container=container
// start thread
boolean addedToContainer = false;
boolean started = false;
try {
container.onStart(this); // may throw,加入跟踪container=TrackingRootContainer
addedToContainer = true;
// scoped values may be inherited
inheritScopedValueBindings(container);
// submit task to run thread
submitRunContinuation(); //提交到scheduler执行
started = true;
} finally {
if (!started) {
setState(TERMINATED);
afterTerminate(addedToContainer, /*executed*/false); //线程退出的正常清理工作:notifyJvmtiUnmount、termination.countDown、threadContainer().onExit、clearReferences
}
}
}
private void submitRunContinuation() {
try {
scheduler.execute(runContinuation); //scheduler=ForkJoinPool,runContinuation=VirtualThread::runContinuation
} catch (RejectedExecutionException ree) {
submitFailed(ree); //发送JFR事件
throw ree;
}
}
private void runContinuation() {
// the carrier must be a platform thread
if (Thread.currentThread().isVirtual()) {
throw new WrongThreadException();
}
// set state to RUNNING
int initialState = state();
if (initialState == STARTED && compareAndSetState(STARTED, RUNNING)) {
// first run
} else if (initialState == RUNNABLE && compareAndSetState(RUNNABLE, RUNNING)) {
// consume parking permit
setParkPermit(false);
} else {
// not runnable
return;
}
// notify JVMTI before mount
notifyJvmtiMount(/*hide*/true);
try {
cont.run(); //这里面大多会因为有阻塞而挂起
} finally {
if (cont.isDone()) {
afterTerminate();
} else {
afterYield(); //一般协程的run都会有挂起,然后走到这里
}
}
}
- 进入协程enterSpecial
enterSpecial会初始化协程的上下文,然后去执行真正的target.run
public final void run() {
while (true) {
mount();
JLA.setScopedValueCache(scopedValueCache);
if (done)
throw new IllegalStateException("Continuation terminated");
Thread t = currentCarrierThread();
if (parent != null) {
if (parent != JLA.getContinuation(t))
throw new IllegalStateException();
} else
this.parent = JLA.getContinuation(t); //上一层协程
JLA.setContinuation(t, this);
try {
boolean isVirtualThread = (scope == JLA.virtualThreadContinuationScope());
if (!isStarted()) { // is this the first run? (at this point we know !done)
enterSpecial(this, false, isVirtualThread); //native里面会调用Continuation.enter,真正的去执行target.run
} else {
assert !isEmpty();
enterSpecial(this, true, isVirtualThread); //重新进入,先恢复栈帧再执行target.run
}
} finally { //enterSpecial里遇到阻塞yield,在freeze_internal里保存协程的栈帧到内存后,会返回到这里。退出这个run,协程被正式挂机
fence();
try {
assert isEmpty() == done : "empty: " + isEmpty() + " done: " + done + " cont: " + Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(this));
JLA.setContinuation(currentCarrierThread(), this.parent);
if (parent != null)
parent.child = null;
postYieldCleanup();
unmount();
if (PRESERVE_SCOPED_VALUE_CACHE) {
scopedValueCache = JLA.scopedValueCache();
} else {
scopedValueCache = null;
}
JLA.setScopedValueCache(null);
} catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1); }
}
// we're now in the parent continuation
assert yieldInfo == null || yieldInfo instanceof ContinuationScope;
if (yieldInfo == null || yieldInfo == scope) {
this.parent = null;
this.yieldInfo = null;
return; //target.run里没有挂起操作,正常结束退出
} else {
parent.child = this;
parent.yield0((ContinuationScope)yieldInfo, this);
parent.child = null;
}
}
}
private static void enter(Continuation c, boolean isContinue) {
// This method runs in the "entry frame".
// A yield jumps to this method's caller as if returning from this method.
try {
c.enter0();
} finally {
c.finish();
}
}
private void enter0() {
target.run();
}
- 挂起协程VirtualThread.park
在target.run中,遇到阻塞时(比如LockSupport.park),会调用VirtualThread.park。
public void VirtualThread::park() {
assert Thread.currentThread() == this;
// complete immediately if parking permit available or interrupted
if (getAndSetParkPermit(false) || interrupted)
return;
// park the thread
boolean yielded = false;
setState(PARKING);
try {
yielded = yieldContinuation(); // may throw
} finally {
assert (Thread.currentThread() == this) && (yielded == (state() == RUNNING));
if (!yielded) {
assert state() == PARKING;
setState(RUNNING);
}
}
// park on the carrier thread when pinned
if (!yielded) {
parkOnCarrierThread(false, 0);
}
}
private boolean VirtualThread::yieldContinuation() {
// unmount
notifyJvmtiUnmount(/*hide*/true);
unmount();
try {
return Continuation.yield(VTHREAD_SCOPE);
} finally {
// re-mount
mount();
notifyJvmtiMount(/*hide*/false);
}
}
public static boolean Continuation::yield(ContinuationScope scope) { //确认scope存在则继续调yield0
Continuation cont = JLA.getContinuation(currentCarrierThread());
Continuation c;
for (c = cont; c != null && c.scope != scope; c = c.parent)
;
if (c == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Not in scope " + scope);
return cont.yield0(scope, null);
}
private boolean Continuation::yield0(ContinuationScope scope, Continuation child) {
preempted = false;
if (scope != this.scope)
this.yieldInfo = scope;
int res = doYield(); //真正执行yield,native里保存这一帧之前的栈帧信息到内存
U.storeFence(); // needed to prevent certain transformations by the compiler
assert scope != this.scope || yieldInfo == null : "scope: " + scope + " this.scope: " + this.scope + " yieldInfo: " + yieldInfo + " res: " + res;
assert yieldInfo == null || scope == this.scope || yieldInfo instanceof Integer : "scope: " + scope + " this.scope: " + this.scope + " yieldInfo: " + yieldInfo + " res: " + res;
if (child != null) { // TODO: ugly
if (res != 0) {
child.yieldInfo = res;
} else if (yieldInfo != null) {
assert yieldInfo instanceof Integer;
child.yieldInfo = yieldInfo;
} else {
child.yieldInfo = res;
}
this.yieldInfo = null;
} else {
if (res == 0 && yieldInfo != null) {
res = (Integer)yieldInfo;
}
this.yieldInfo = null;
if (res == 0)
onContinue(); //空操作
else
onPinned0(res);
}
assert yieldInfo == null;
return res == 0;
}
- 重启协程VirtualThread.unpark
public void unpark() {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
if (!getAndSetParkPermit(true) && currentThread != this) {
int s = state();
if (s == PARKED && compareAndSetState(PARKED, RUNNABLE)) {
if (currentThread instanceof VirtualThread vthread) {
vthread.switchToCarrierThread();
try {
submitRunContinuation(); //再次进入协程Continuation.run
} finally {
switchToVirtualThread(vthread);
}
} else {
submitRunContinuation();
}
} else if (s == PINNED) {
// unpark carrier thread when pinned.
synchronized (carrierThreadAccessLock()) {
Thread carrier = carrierThread;
if (carrier != null && state() == PINNED) {
U.unpark(carrier);
}
}
}
}
}
虚拟机实现
协程的栈桢在虚拟机中维护,所以各种切换动作都是在虚拟机里实现的。
- enterSpecial
enterSpecial这个native方法的生成代码在src\hotspot\cpu\x86\sharedRuntime_x86_64.cpp
static void gen_continuation_enter(MacroAssembler* masm,
const VMRegPair* regs,
int& exception_offset,
OopMapSet* oop_maps,
int& frame_complete,
int& stack_slots,
int& interpreted_entry_offset,
int& compiled_entry_offset) {
// enterSpecial(Continuation c, boolean isContinue, boolean isVirtualThread)
int pos_cont_obj = 0;
int pos_is_cont = 1;
int pos_is_virtual = 2;
// The platform-specific calling convention may present the arguments in various registers.
// To simplify the rest of the code, we expect the arguments to reside at these known
// registers, and we additionally check the placement here in case calling convention ever
// changes.
Register reg_cont_obj = c_rarg1;
Register reg_is_cont = c_rarg2;
Register reg_is_virtual = c_rarg3;
check_continuation_enter_argument(regs[pos_cont_obj].first(), reg_cont_obj, "Continuation object");
check_continuation_enter_argument(regs[pos_is_cont].first(), reg_is_cont, "isContinue");
check_continuation_enter_argument(regs[pos_is_virtual].first(), reg_is_virtual, "isVirtualThread");
// Utility methods kill rax, make sure there are no collisions
assert_different_registers(rax, reg_cont_obj, reg_is_cont, reg_is_virtual);
AddressLiteral resolve(SharedRuntime::get_resolve_static_call_stub(),
relocInfo::static_call_type);
address start = __ pc();
Label L_thaw, L_exit;
// i2i entry used at interp_only_mode only
interpreted_entry_offset = __ pc() - start; //解释执行的代码入口
{
#ifdef ASSERT
Label is_interp_only;
__ cmpb(Address(r15_thread, JavaThread::interp_only_mode_offset()), 0);
__ jcc(Assembler::notEqual, is_interp_only);
__ stop("enterSpecial interpreter entry called when not in interp_only_mode");
__ bind(is_interp_only);
#endif
__ pop(rax); // return address
// Read interpreter arguments into registers (this is an ad-hoc i2c adapter)
__ movptr(c_rarg1, Address(rsp, Interpreter::stackElementSize*2));
__ movl(c_rarg2, Address(rsp, Interpreter::stackElementSize*1));
__ movl(c_rarg3, Address(rsp, Interpreter::stackElementSize*0));
__ andptr(rsp, -16); // Ensure compiled code always sees stack at proper alignment
__ push(rax); // return address
__ push_cont_fastpath();
__ enter(); //开启下一帧
stack_slots = 2; // will be adjusted in setup
OopMap* map = continuation_enter_setup(masm, stack_slots); //为Continuation.enter作准备,塞一个ContinuationEntry到栈帧上
// The frame is complete here, but we only record it for the compiled entry, so the frame would appear unsafe,
// but that's okay because at the very worst we'll miss an async sample, but we're in interp_only_mode anyway.
__ verify_oop(reg_cont_obj);
fill_continuation_entry(masm, reg_cont_obj, reg_is_virtual); //填充ContinuationEntry数据
// If continuation, call to thaw. Otherwise, resolve the call and exit.
__ testptr(reg_is_cont, reg_is_cont);
__ jcc(Assembler::notZero, L_thaw); //不是第一次走解冻流程
// --- Resolve path
// Make sure the call is patchable
__ align(BytesPerWord, __ offset() + NativeCall::displacement_offset);
// Emit stub for static call
CodeBuffer* cbuf = masm->code_section()->outer();
address stub = CompiledStaticCall::emit_to_interp_stub(*cbuf, __ pc());
if (stub == nullptr) {
fatal("CodeCache is full at gen_continuation_enter");
}
__ call(resolve); //调用Continuation.enter
oop_maps->add_gc_map(__ pc() - start, map);
__ post_call_nop();
__ jmp(L_exit);
}
// compiled entry
__ align(CodeEntryAlignment);
compiled_entry_offset = __ pc() - start; //编译执行的代码入口
__ enter();
stack_slots = 2; // will be adjusted in setup
OopMap* map = continuation_enter_setup(masm, stack_slots);
// Frame is now completed as far as size and linkage.
frame_complete = __ pc() - start;
__ verify_oop(reg_cont_obj);
fill_continuation_entry(masm, reg_cont_obj, reg_is_virtual);
// If isContinue, call to thaw. Otherwise, call Continuation.enter(Continuation c, boolean isContinue)
__ testptr(reg_is_cont, reg_is_cont);
__ jccb(Assembler::notZero, L_thaw);
// --- call Continuation.enter(Continuation c, boolean isContinue)
// Make sure the call is patchable
__ align(BytesPerWord, __ offset() + NativeCall::displacement_offset);
// Emit stub for static call
CodeBuffer* cbuf = masm->code_section()->outer();
address stub = CompiledStaticCall::emit_to_interp_stub(*cbuf, __ pc());
if (stub == nullptr) {
fatal("CodeCache is full at gen_continuation_enter");
}
// The call needs to be resolved. There's a special case for this in
// SharedRuntime::find_callee_info_helper() which calls
// LinkResolver::resolve_continuation_enter() which resolves the call to
// Continuation.enter(Continuation c, boolean isContinue).
__ call(resolve);
oop_maps->add_gc_map(__ pc() - start, map);
__ post_call_nop();
__ jmpb(L_exit);
// --- Thawing path
__ bind(L_thaw); //第二次进入协程解冻流程
__ call(RuntimeAddress(StubRoutines::cont_thaw()));
ContinuationEntry::_return_pc_offset = __ pc() - start;
oop_maps->add_gc_map(__ pc() - start, map->deep_copy());
__ post_call_nop();
// --- Normal exit (resolve/thawing)
__ bind(L_exit);
continuation_enter_cleanup(masm);
__ pop(rbp);
__ ret(0);
// --- Exception handling path
exception_offset = __ pc() - start; //异常处理
continuation_enter_cleanup(masm);
__ pop(rbp);
__ movptr(c_rarg0, r15_thread);
__ movptr(c_rarg1, Address(rsp, 0)); // return address
// rax still holds the original exception oop, save it before the call
__ push(rax);
__ call_VM_leaf(CAST_FROM_FN_PTR(address, SharedRuntime::exception_handler_for_return_address), 2);
__ movptr(rbx, rax);
// Continue at exception handler:
// rax: exception oop
// rbx: exception handler
// rdx: exception pc
__ pop(rax);
__ verify_oop(rax);
__ pop(rdx);
__ jmp(rbx);
}
- doYield
生成代码在gen_continuation_yield。
static void gen_continuation_yield(MacroAssembler* masm,
const VMRegPair* regs,
OopMapSet* oop_maps,
int& frame_complete,
int& stack_slots,
int& compiled_entry_offset) {
enum layout {
rbp_off,
rbpH_off,
return_off,
return_off2,
framesize // inclusive of return address
};
stack_slots = framesize / VMRegImpl::slots_per_word;
assert(stack_slots == 2, "recheck layout");
address start = __ pc();
compiled_entry_offset = __ pc() - start; //编译执行的代码入口
__ enter(); //开启新栈帧
address the_pc = __ pc();
frame_complete = the_pc - start;
// This nop must be exactly at the PC we push into the frame info.
// We use this nop for fast CodeBlob lookup, associate the OopMap
// with it right away.
__ post_call_nop();
OopMap* map = new OopMap(framesize, 1);
oop_maps->add_gc_map(frame_complete, map);
__ set_last_Java_frame(rsp, rbp, the_pc, rscratch1);
__ movptr(c_rarg0, r15_thread);
__ movptr(c_rarg1, rsp);
__ call_VM_leaf(Continuation::freeze_entry(), 2); //这个函数地址最终会调用到freeze_internal保存当前协程的桢到内存
__ reset_last_Java_frame(true); //恢复最后一个java桢
Label L_pinned;
__ testptr(rax, rax);
__ jcc(Assembler::notZero, L_pinned);
__ movptr(rsp, Address(r15_thread, JavaThread::cont_entry_offset())); //将rsp恢复到调用Continuation.enter之前的栈帧(保存在ContinuationEntry)
continuation_enter_cleanup(masm);
__ pop(rbp); //恢复到协程入口Continuation:run那一帧
__ ret(0); //回到
__ bind(L_pinned);
// Pinned, return to caller
// handle pending exception thrown by freeze
__ cmpptr(Address(r15_thread, Thread::pending_exception_offset()), NULL_WORD);
Label ok;
__ jcc(Assembler::equal, ok);
__ leave();
__ jump(RuntimeAddress(StubRoutines::forward_exception_entry()));
__ bind(ok);
__ leave();
__ ret(0);
}
- freeze_internal
代码在src\hotspot\share\runtime\continuationFreezeThaw.cpp。这个函数会找到当前线程上的最后一个ContinuationEntry,将从这里开始的栈帧全部复制到内存中。 - thaw
通过Continuation上保存的栈信息StackChunk tail,从内存中恢复栈帧。 - pin&unpin&ispined
这三个native接口只是维护ContinuationEntry对象的引用计算状态,代码在src\hotspot\share\runtime\continuation.cpp
bool is_pinned() { return _pin_count > 0; }
bool pin() {
if (_pin_count == UINT_MAX) return false;
_pin_count++;
return true;
}
bool unpin() {
if (_pin_count == 0) return false;
_pin_count--;
return true;
}
微信扫描下方的二维码阅读本文

0 Comments