前言
Gossip字面是流言、八卦的意思。Gossip协议是一种去中心化的传播协议。
Gossip协议详情可以参考这里https://www.cs.cornell.edu/home/rvr/papers/flowgossip.pdf
Gossip协议并没有一个官方的、标准的协议文本,所以不同项目里的实现会有点差异。
BTC、ETH等加密货币用的是Gossip,分布式数据库Apache Cassandra、Redis集群也是用的Gossip。
有三种信息传播模式:
- Direct Mail
全节点广播 - Anti-entropy
随机广播给临近节点 - Rumor Mongering
随机广播给临近节点,临近节点收到消息后继续广播这个消息
Redis项目的Gossip实现
Redis Cluster需要传播的信息:各个节点的存活状态、主从关系、分配的槽位。数据内容并不大,采用的是Anti-entropy模式。
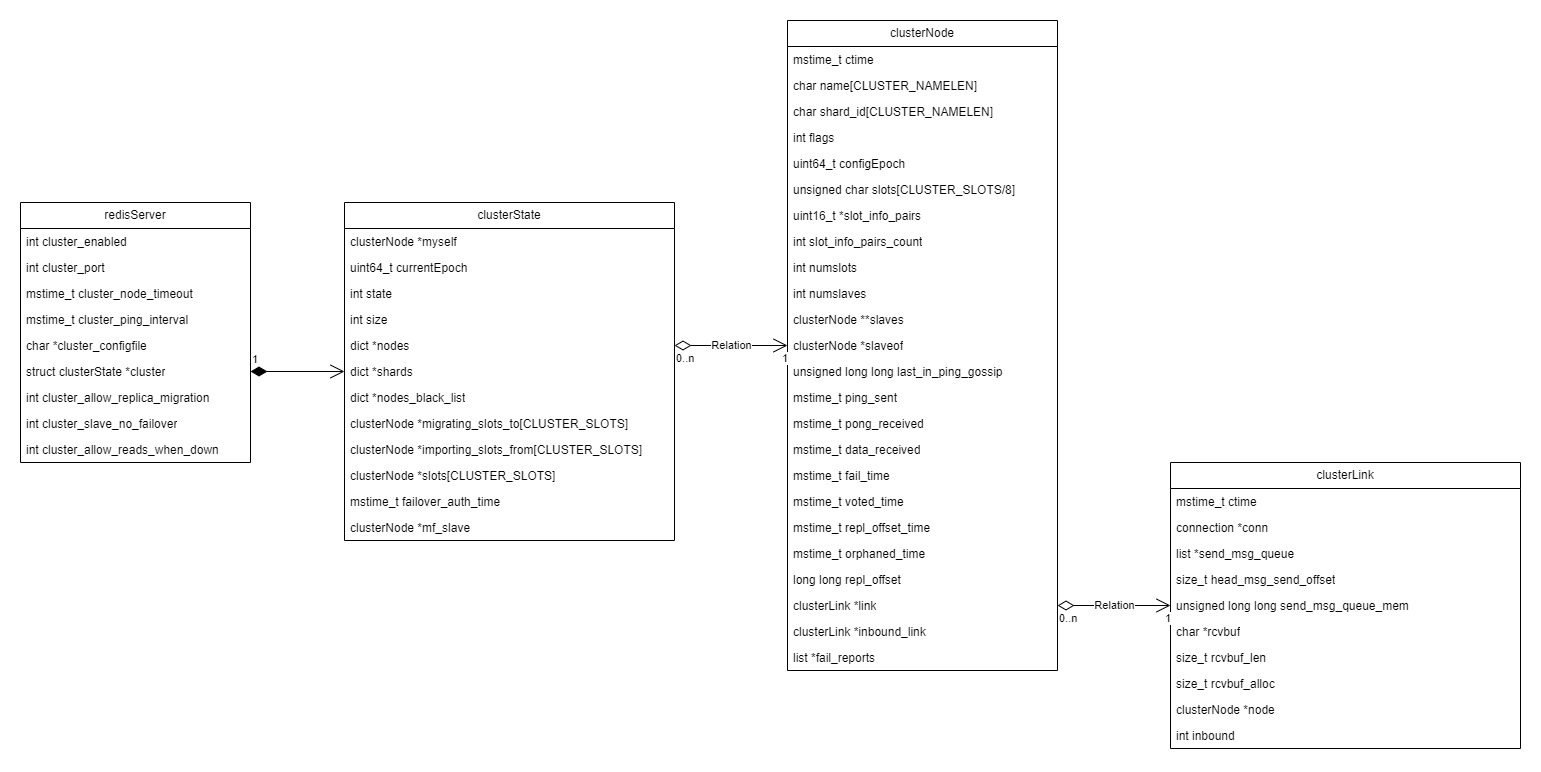
上图是Redis中Cluster相关的数据结构(只列了比较重要的Cluster相关的属性)。集群实现相关的代码在cluster_legacy.c。
Redis全局对象redisServer上有一个clusterState维护了集群的拓扑状态,其中myself是本节点状态,nodes是和本节点有连接的其他节点clusterNode。clusterLink代表每个clusterNode关联的TCP连接上的状态。send_msg_queue是该连接上等待发送的消息(IO主线程负责send),rcvbuf是该连接收到的待处理的消息(IO主线程读到的消息缓存到这里)。
节点状态包括
/* Cluster node flags and macros. */
#define CLUSTER_NODE_MASTER 1 /* The node is a master */
#define CLUSTER_NODE_SLAVE 2 /* The node is a slave */
#define CLUSTER_NODE_PFAIL 4 /* Failure? Need acknowledge */
#define CLUSTER_NODE_FAIL 8 /* The node is believed to be malfunctioning */
#define CLUSTER_NODE_MYSELF 16 /* This node is myself */
#define CLUSTER_NODE_HANDSHAKE 32 /* We have still to exchange the first ping */
#define CLUSTER_NODE_NOADDR 64 /* We don't know the address of this node */
#define CLUSTER_NODE_MEET 128 /* Send a MEET message to this node */
#define CLUSTER_NODE_MIGRATE_TO 256 /* Master eligible for replica migration. */
#define CLUSTER_NODE_NOFAILOVER 512 /* Slave will not try to failover. */
#define CLUSTER_NODE_EXTENSIONS_SUPPORTED 1024 /* This node supports extensions. */
Redis节点主动逻辑
clusterCron函数是Cluster主动逻辑的总入口,每秒被调用10次。主要的工作包括:
- 随机找1个节点发送ping消息
发送PING消息clusterSendPing - 收集CLUSTER_NODE_PFAIL节点的投票数,确认是否需要标记为CLUSTER_NODE_FAIL
投票超半数needed_quorum = (server.cluster->size / 2) + 1,调用clusterSendFail广播FAIL消息 - 如果是备节点,检查是否需要重连主节点
这个是Redis特有的备份机制,和Gossip协议无关。replicationSetMaster - 重置超时的手动故障转移
这个是Redis特有的备份机制,和Gossip协议无关。
cluster failover命令可以手动触发故障转移,这里检查故障转移超时就重置。函数是resetManualFailover - 检查投票设置本节点的状态
本节点可达的master过半,就设置为CLUSTER_OK,否则CLUSTER_FAIL
详细代码如下
/* This is executed 10 times every second */
void clusterCron(void) {
dictIterator *di;
dictEntry *de;
int update_state = 0;
int orphaned_masters; /* How many masters there are without ok slaves. */
int max_slaves; /* Max number of ok slaves for a single master. */
int this_slaves; /* Number of ok slaves for our master (if we are slave). */
mstime_t min_pong = 0, now = mstime();
clusterNode *min_pong_node = NULL;
static unsigned long long iteration = 0;
mstime_t handshake_timeout;
iteration++; /* Number of times this function was called so far. */
clusterUpdateMyselfHostname();
/* The handshake timeout is the time after which a handshake node that was
* not turned into a normal node is removed from the nodes. Usually it is
* just the NODE_TIMEOUT value, but when NODE_TIMEOUT is too small we use
* the value of 1 second. */
handshake_timeout = server.cluster_node_timeout;
if (handshake_timeout < 1000) handshake_timeout = 1000;
/* Clear so clusterNodeCronHandleReconnect can count the number of nodes in PFAIL. */
server.cluster->stats_pfail_nodes = 0;
/* Run through some of the operations we want to do on each cluster node. */
di = dictGetSafeIterator(server.cluster->nodes);
while((de = dictNext(di)) != NULL) {
clusterNode *node = dictGetVal(de);
/* We free the inbound or outboud link to the node if the link has an
* oversized message send queue and immediately try reconnecting. */
clusterNodeCronFreeLinkOnBufferLimitReached(node);
/* The protocol is that function(s) below return non-zero if the node was
* terminated.
*/
if(clusterNodeCronHandleReconnect(node, handshake_timeout, now)) continue;
}
dictReleaseIterator(di);
/* Ping some random node 1 time every 10 iterations, so that we usually ping
* one random node every second. */
if (!(iteration % 10)) {
int j;
/* Check a few random nodes and ping the one with the oldest
* pong_received time. */
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
de = dictGetRandomKey(server.cluster->nodes);
clusterNode *this = dictGetVal(de);
/* Don't ping nodes disconnected or with a ping currently active. */
if (this->link == NULL || this->ping_sent != 0) continue;
if (this->flags & (CLUSTER_NODE_MYSELF|CLUSTER_NODE_HANDSHAKE))
continue;
if (min_pong_node == NULL || min_pong > this->pong_received) {
min_pong_node = this;
min_pong = this->pong_received;
}
}
if (min_pong_node) {
serverLog(LL_DEBUG,"Pinging node %.40s", min_pong_node->name);
clusterSendPing(min_pong_node->link, CLUSTERMSG_TYPE_PING);
}
}
/* Iterate nodes to check if we need to flag something as failing.
* This loop is also responsible to:
* 1) Check if there are orphaned masters (masters without non failing
* slaves).
* 2) Count the max number of non failing slaves for a single master.
* 3) Count the number of slaves for our master, if we are a slave. */
orphaned_masters = 0;
max_slaves = 0;
this_slaves = 0;
di = dictGetSafeIterator(server.cluster->nodes);
while((de = dictNext(di)) != NULL) {
clusterNode *node = dictGetVal(de);
now = mstime(); /* Use an updated time at every iteration. */
if (node->flags &
(CLUSTER_NODE_MYSELF|CLUSTER_NODE_NOADDR|CLUSTER_NODE_HANDSHAKE))
continue;
/* Orphaned master check, useful only if the current instance
* is a slave that may migrate to another master. */
if (nodeIsSlave(myself) && clusterNodeIsMaster(node) && !nodeFailed(node)) {
int okslaves = clusterCountNonFailingSlaves(node);
/* A master is orphaned if it is serving a non-zero number of
* slots, have no working slaves, but used to have at least one
* slave, or failed over a master that used to have slaves. */
if (okslaves == 0 && node->numslots > 0 &&
node->flags & CLUSTER_NODE_MIGRATE_TO)
{
orphaned_masters++;
}
if (okslaves > max_slaves) max_slaves = okslaves;
if (myself->slaveof == node)
this_slaves = okslaves;
}
/* If we are not receiving any data for more than half the cluster
* timeout, reconnect the link: maybe there is a connection
* issue even if the node is alive. */
mstime_t ping_delay = now - node->ping_sent;
mstime_t data_delay = now - node->data_received;
if (node->link && /* is connected */
now - node->link->ctime >
server.cluster_node_timeout && /* was not already reconnected */
node->ping_sent && /* we already sent a ping */
/* and we are waiting for the pong more than timeout/2 */
ping_delay > server.cluster_node_timeout/2 &&
/* and in such interval we are not seeing any traffic at all. */
data_delay > server.cluster_node_timeout/2)
{
/* Disconnect the link, it will be reconnected automatically. */
freeClusterLink(node->link);
}
/* If we have currently no active ping in this instance, and the
* received PONG is older than half the cluster timeout, send
* a new ping now, to ensure all the nodes are pinged without
* a too big delay. */
mstime_t ping_interval = server.cluster_ping_interval ?
server.cluster_ping_interval : server.cluster_node_timeout/2;
if (node->link &&
node->ping_sent == 0 &&
(now - node->pong_received) > ping_interval)
{
clusterSendPing(node->link, CLUSTERMSG_TYPE_PING);
continue;
}
/* If we are a master and one of the slaves requested a manual
* failover, ping it continuously. */
if (server.cluster->mf_end &&
clusterNodeIsMaster(myself) &&
server.cluster->mf_slave == node &&
node->link)
{
clusterSendPing(node->link, CLUSTERMSG_TYPE_PING);
continue;
}
/* Check only if we have an active ping for this instance. */
if (node->ping_sent == 0) continue;
/* Check if this node looks unreachable.
* Note that if we already received the PONG, then node->ping_sent
* is zero, so can't reach this code at all, so we don't risk of
* checking for a PONG delay if we didn't sent the PING.
*
* We also consider every incoming data as proof of liveness, since
* our cluster bus link is also used for data: under heavy data
* load pong delays are possible. */
mstime_t node_delay = (ping_delay < data_delay) ? ping_delay :
data_delay;
if (node_delay > server.cluster_node_timeout) {
/* Timeout reached. Set the node as possibly failing if it is
* not already in this state. */
if (!(node->flags & (CLUSTER_NODE_PFAIL|CLUSTER_NODE_FAIL))) {
node->flags |= CLUSTER_NODE_PFAIL;
update_state = 1;
if (clusterNodeIsMaster(myself) && server.cluster->size == 1) {
markNodeAsFailingIfNeeded(node);
} else {
serverLog(LL_DEBUG,"*** NODE %.40s possibly failing", node->name);
}
}
}
}
dictReleaseIterator(di);
/* If we are a slave node but the replication is still turned off,
* enable it if we know the address of our master and it appears to
* be up. */
if (nodeIsSlave(myself) &&
server.masterhost == NULL &&
myself->slaveof &&
nodeHasAddr(myself->slaveof))
{
replicationSetMaster(myself->slaveof->ip, getNodeDefaultReplicationPort(myself->slaveof));
}
/* Abort a manual failover if the timeout is reached. */
manualFailoverCheckTimeout();
if (nodeIsSlave(myself)) {
clusterHandleManualFailover();
if (!(server.cluster_module_flags & CLUSTER_MODULE_FLAG_NO_FAILOVER))
clusterHandleSlaveFailover();
/* If there are orphaned slaves, and we are a slave among the masters
* with the max number of non-failing slaves, consider migrating to
* the orphaned masters. Note that it does not make sense to try
* a migration if there is no master with at least *two* working
* slaves. */
if (orphaned_masters && max_slaves >= 2 && this_slaves == max_slaves &&
server.cluster_allow_replica_migration)
clusterHandleSlaveMigration(max_slaves);
}
if (update_state || server.cluster->state == CLUSTER_FAIL)
clusterUpdateState();
}
Redis节点被动逻辑
clusterProcessPacket这个函数是根据收到的请求消息,更新本节点状态,然后给出对应的应答消息。这部分比较简单,不详细看。
比特币网络
比特币的P2P网络在节点管理上,和Redis大同小异。不过他使用Direct Mail模式,消息全量发给临近节点。
和Redis通过PING、PONG消息传播网络拓扑状态不同。比特币的PING、PONG消息上只有一个随机数。P2P网络时序如下:
- 发送握手协议
VER、VERACK - 向临近节点拉取节点列表
GETADDR - 心跳检查存活状态
PING、PONG - 广播业务消息
TX、HEADS,收到的节点需要转发
从上面可以看出,比特币网络的Gossip协议比Redis的要复杂一点,重复消息也很多,每个节点都有消息抑制措施。
微信扫描下方的二维码阅读本文

0 Comments