虚拟文件系统
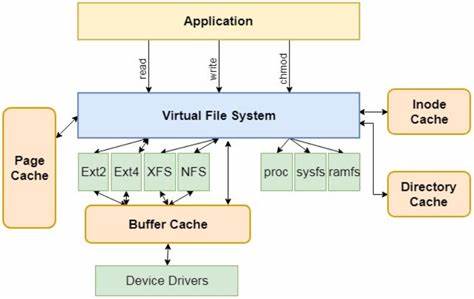
Linux的文件系统有两大特色:
- 虚拟文件系统接口
VFS(Virtual File System,虚拟文件系统)。Linux内核并没有实现一个特定的文件系统,而是定义了一组文件系统相关的接口file_operations。只要实现了这组接口的文件系统(比如ext4、nfs、proc等),都可以挂载进内核使用。接口定义在include\linux\fs.h
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
fop_flags_t fop_flags;
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*read_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);
ssize_t (*write_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);
int (*iopoll)(struct kiocb *kiocb, struct io_comp_batch *,
unsigned int flags);
int (*iterate_shared) (struct file *, struct dir_context *);
__poll_t (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id);
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*fsync) (struct file *, loff_t, loff_t, int datasync);
int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int);
int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area)(struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);
int (*check_flags)(int);
int (*flock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*splice_write)(struct pipe_inode_info *, struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, unsigned int);
ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct file *, loff_t *, struct pipe_inode_info *, size_t, unsigned int);
void (*splice_eof)(struct file *file);
int (*setlease)(struct file *, int, struct file_lease **, void **);
long (*fallocate)(struct file *file, int mode, loff_t offset,
loff_t len);
void (*show_fdinfo)(struct seq_file *m, struct file *f);
#ifndef CONFIG_MMU
unsigned (*mmap_capabilities)(struct file *);
#endif
ssize_t (*copy_file_range)(struct file *, loff_t, struct file *,
loff_t, size_t, unsigned int);
loff_t (*remap_file_range)(struct file *file_in, loff_t pos_in,
struct file *file_out, loff_t pos_out,
loff_t len, unsigned int remap_flags);
int (*fadvise)(struct file *, loff_t, loff_t, int);
int (*uring_cmd)(struct io_uring_cmd *ioucmd, unsigned int issue_flags);
int (*uring_cmd_iopoll)(struct io_uring_cmd *, struct io_comp_batch *,
unsigned int poll_flags);
} __randomize_layout;
- 一切皆文件
不只普通的文件可以看做文件描述符,几乎所有其他对象都被抽象成了文件(比如字符设备、块设备、套接字、管道等),使用同一套接口操作。
struct fd {
struct file *file;
unsigned int flags;
};
文件系统常见概念
- 超级块
超级块super_block是文件系统的入口,文件系统的所有元数据都记录在这里。定义如下
struct super_block {
struct list_head s_list; /* Keep this first */
dev_t s_dev; /* search index; _not_ kdev_t */
unsigned char s_blocksize_bits;
unsigned long s_blocksize;
loff_t s_maxbytes; /* Max file size */
struct file_system_type *s_type;
const struct super_operations *s_op;
const struct dquot_operations *dq_op;
const struct quotactl_ops *s_qcop;
const struct export_operations *s_export_op;
unsigned long s_flags;
unsigned long s_iflags; /* internal SB_I_* flags */
unsigned long s_magic;
struct dentry *s_root;
struct rw_semaphore s_umount;
int s_count;
atomic_t s_active;
......
const struct dentry_operations *s_d_op; /* default d_op for dentries */
......
struct list_head s_inodes; /* all inodes */
......
} __randomize_layout;
- inode
inode索引代表一个文件,记录了文件和磁盘块的对应关系。ls命令看到的文件状态,也都记录在这里。
struct inode {
umode_t i_mode;
unsigned short i_opflags;
kuid_t i_uid;
kgid_t i_gid;
unsigned int i_flags;
......
const struct inode_operations *i_op;
struct super_block *i_sb;
struct address_space *i_mapping;
......
dev_t i_rdev;
loff_t i_size;
time64_t i_atime_sec;
time64_t i_mtime_sec;
time64_t i_ctime_sec;
u32 i_atime_nsec;
u32 i_mtime_nsec;
u32 i_ctime_nsec;
u32 i_generation;
spinlock_t i_lock; /* i_blocks, i_bytes, maybe i_size */
unsigned short i_bytes;
u8 i_blkbits;
enum rw_hint i_write_hint;
blkcnt_t i_blocks;
......
struct list_head i_lru; /* inode LRU list */
struct list_head i_sb_list;
struct list_head i_wb_list; /* backing dev writeback list */
union {
struct hlist_head i_dentry;
struct rcu_head i_rcu;
};
atomic64_t i_version;
atomic64_t i_sequence; /* see futex */
atomic_t i_count;
atomic_t i_dio_count;
atomic_t i_writecount;
union {
const struct file_operations *i_fop; /* former ->i_op->default_file_ops */
void (*free_inode)(struct inode *);
};
struct file_lock_context *i_flctx;
struct address_space i_data;
struct list_head i_devices;
union {
struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe;
struct cdev *i_cdev;
char *i_link;
unsigned i_dir_seq;
};
......
void *i_private; /* fs or device private pointer */
} __randomize_layout;
- 目录
dentry结构代表了一个目录项
struct dentry {
/* RCU lookup touched fields */
unsigned int d_flags; /* protected by d_lock */
seqcount_spinlock_t d_seq; /* per dentry seqlock */
struct hlist_bl_node d_hash; /* lookup hash list */
struct dentry *d_parent; /* parent directory */
struct qstr d_name;
struct inode *d_inode; /* Where the name belongs to - NULL is
* negative */
unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN]; /* small names */
/* --- cacheline 1 boundary (64 bytes) was 32 bytes ago --- */
/* Ref lookup also touches following */
const struct dentry_operations *d_op;
struct super_block *d_sb; /* The root of the dentry tree */
unsigned long d_time; /* used by d_revalidate */
void *d_fsdata; /* fs-specific data */
/* --- cacheline 2 boundary (128 bytes) --- */
struct lockref d_lockref; /* per-dentry lock and refcount
* keep separate from RCU lookup area if
* possible!
*/
union {
struct list_head d_lru; /* LRU list */
wait_queue_head_t *d_wait; /* in-lookup ones only */
};
struct hlist_node d_sib; /* child of parent list */
struct hlist_head d_children; /* our children */
/*
* d_alias and d_rcu can share memory
*/
union {
struct hlist_node d_alias; /* inode alias list */
struct hlist_bl_node d_in_lookup_hash; /* only for in-lookup ones */
struct rcu_head d_rcu;
} d_u;
};
- 文件
file代表了一个打开的文件,对应一个fd。
struct file {
union {
/* fput() uses task work when closing and freeing file (default). */
struct callback_head f_task_work;
/* fput() must use workqueue (most kernel threads). */
struct llist_node f_llist;
unsigned int f_iocb_flags;
};
/*
* Protects f_ep, f_flags.
* Must not be taken from IRQ context.
*/
spinlock_t f_lock;
fmode_t f_mode;
atomic_long_t f_count;
struct mutex f_pos_lock;
loff_t f_pos;
unsigned int f_flags;
struct fown_struct f_owner;
const struct cred *f_cred;
struct file_ra_state f_ra;
struct path f_path;
struct inode *f_inode; /* cached value */
const struct file_operations *f_op;
u64 f_version;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *f_security;
#endif
/* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */
void *private_data;
#ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL
/* Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file */
struct hlist_head *f_ep;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL */
struct address_space *f_mapping;
errseq_t f_wb_err;
errseq_t f_sb_err; /* for syncfs */
} __randomize_layout
__attribute__((aligned(4))); /* lest something weird decides that 2 is OK */
以上定义中,有一些*_operations结尾的属性。这些结构中都仅仅只有一些函数指针,是内核中实现插件的方式。
文件系统将创建好的super_block、dentry、inode、file对象返回之前,会将对应的operations接口设置好。这样就做到了对调用者(这里是内核)隐藏具体的实现细节。
文件系统挂载
以下都以ext4文件系统为例。
- 定义内核模块
把ext4写到内核的模块段.modinfo中
static struct file_system_type ext4_fs_type = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = "ext4",
.init_fs_context = ext4_init_fs_context, //文件系统初始化入口
.parameters = ext4_param_specs,
.kill_sb = ext4_kill_sb,
.fs_flags = FS_REQUIRES_DEV | FS_ALLOW_IDMAP,
};
MODULE_ALIAS_FS("ext4");
- 文件系统上下文
这里的上下文就是文件系统实现相关的一些元数据。
int ext4_init_fs_context(struct fs_context *fc)
{
struct ext4_fs_context *ctx;
ctx = kzalloc(sizeof(struct ext4_fs_context), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!ctx)
return -ENOMEM;
fc->fs_private = ctx; //文件系统上下文
fc->ops = &ext4_context_ops;
return 0;
}
const struct file_operations ext4_file_operations = {
.llseek = ext4_llseek,
.read_iter = ext4_file_read_iter,
.write_iter = ext4_file_write_iter,
.iopoll = iocb_bio_iopoll,
.unlocked_ioctl = ext4_ioctl,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_ioctl = ext4_compat_ioctl,
#endif
.mmap = ext4_file_mmap,
.open = ext4_file_open,
.release = ext4_release_file,
.fsync = ext4_sync_file,
.get_unmapped_area = thp_get_unmapped_area,
.splice_read = ext4_file_splice_read,
.splice_write = iter_file_splice_write,
.fallocate = ext4_fallocate,
.fop_flags = FOP_MMAP_SYNC | FOP_BUFFER_RASYNC |
FOP_DIO_PARALLEL_WRITE,
};
const struct inode_operations ext4_file_inode_operations = {
.setattr = ext4_setattr,
.getattr = ext4_file_getattr,
.listxattr = ext4_listxattr,
.get_inode_acl = ext4_get_acl,
.set_acl = ext4_set_acl,
.fiemap = ext4_fiemap,
.fileattr_get = ext4_fileattr_get,
.fileattr_set = ext4_fileattr_set,
};
const struct file_operations ext4_dir_operations = {
.llseek = ext4_dir_llseek,
.read = generic_read_dir,
.iterate_shared = ext4_readdir,
.unlocked_ioctl = ext4_ioctl,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_ioctl = ext4_compat_ioctl,
#endif
.fsync = ext4_sync_file,
.release = ext4_release_dir,
};
- 挂载文件系统
如果Linux没有配置自动加载ext4文件系统,可以通过命令modprobe ext4手动加载
典型文件操作
从用户态函数write开始
- write
用户态write函数调用的系统接口sys_write,sys_write定义在include\linux\syscalls.h
asmlinkage long sys_write(unsigned int fd, const char __user *buf,
size_t count);
- sys_write
sys_write的实现在fs\read_write.c
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(write, unsigned int, fd, const char __user *, buf,
size_t, count)
{
return ksys_write(fd, buf, count);
}
ssize_t ksys_write(unsigned int fd, const char __user *buf, size_t count)
{
struct fd f = fdget_pos(fd);
ssize_t ret = -EBADF;
if (f.file) {
loff_t pos, *ppos = file_ppos(f.file);
if (ppos) {
pos = *ppos;
ppos = &pos;
}
ret = vfs_write(f.file, buf, count, ppos);
if (ret >= 0 && ppos)
f.file->f_pos = pos;
fdput_pos(f);
}
return ret;
}
- vfs_write
vfs_write的实现在fs\read_write.c
ssize_t vfs_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{
ssize_t ret;
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE))
return -EBADF;
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_CAN_WRITE))
return -EINVAL;
if (unlikely(!access_ok(buf, count)))
return -EFAULT;
ret = rw_verify_area(WRITE, file, pos, count);
if (ret)
return ret;
if (count > MAX_RW_COUNT)
count = MAX_RW_COUNT;
file_start_write(file);
if (file->f_op->write) // ext4里这个值是null
ret = file->f_op->write(file, buf, count, pos);
else if (file->f_op->write_iter) //这里file.f_op就是ext4创建file时设置的内部实现接口ext4_file_write_iter
ret = new_sync_write(file, buf, count, pos);
else
ret = -EINVAL;
if (ret > 0) {
fsnotify_modify(file);
add_wchar(current, ret);
}
inc_syscw(current);
file_end_write(file);
return ret;
}
static ssize_t new_sync_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
{
struct kiocb kiocb;
struct iov_iter iter;
ssize_t ret;
init_sync_kiocb(&kiocb, filp);
kiocb.ki_pos = (ppos ? *ppos : 0);
iov_iter_ubuf(&iter, ITER_SOURCE, (void __user *)buf, len);
ret = filp->f_op->write_iter(&kiocb, &iter); //这里file.f_op就是ext4创建file时设置的内部实现接口ext4_file_write_iter
BUG_ON(ret == -EIOCBQUEUED);
if (ret > 0 && ppos)
*ppos = kiocb.ki_pos;
return ret;
}
- ext4_file_write_iter
代码在fs\ext4\file.c
static ssize_t
ext4_file_write_iter(struct kiocb *iocb, struct iov_iter *from)
{
struct inode *inode = file_inode(iocb->ki_filp);
if (unlikely(ext4_forced_shutdown(inode->i_sb)))
return -EIO;
#ifdef CONFIG_FS_DAX
if (IS_DAX(inode))
return ext4_dax_write_iter(iocb, from);
#endif
if (iocb->ki_flags & IOCB_DIRECT) //是否直接IO
return ext4_dio_write_iter(iocb, from); //这里有处理是否阻塞IOCB_NOWAIT
else
return ext4_buffered_write_iter(iocb, from);
}
异步IO
从上面可以看到,ext4只处理了是否直接IO、是否阻塞的标记。并没有异步IO(Asynchronous IO)的接口。但是Linux确实提供了异步IO。
io_getevents的代码在fs\aio.c
static long read_events(struct kioctx *ctx, long min_nr, long nr,
struct io_event __user *event,
ktime_t until)
{
struct hrtimer_sleeper t;
struct aio_waiter w;
long ret = 0, ret2 = 0;
/*
* Note that aio_read_events() is being called as the conditional - i.e.
* we're calling it after prepare_to_wait() has set task state to
* TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE.
*
* But aio_read_events() can block, and if it blocks it's going to flip
* the task state back to TASK_RUNNING.
*
* This should be ok, provided it doesn't flip the state back to
* TASK_RUNNING and return 0 too much - that causes us to spin. That
* will only happen if the mutex_lock() call blocks, and we then find
* the ringbuffer empty. So in practice we should be ok, but it's
* something to be aware of when touching this code.
*/
aio_read_events(ctx, min_nr, nr, event, &ret);
if (until == 0 || ret < 0 || ret >= min_nr)
return ret;
hrtimer_init_sleeper_on_stack(&t, CLOCK_MONOTONIC, HRTIMER_MODE_REL);
if (until != KTIME_MAX) {
hrtimer_set_expires_range_ns(&t.timer, until, current->timer_slack_ns);
hrtimer_sleeper_start_expires(&t, HRTIMER_MODE_REL);
}
init_wait(&w.w);
while (1) {
unsigned long nr_got = ret;
w.min_nr = min_nr - ret;
ret2 = prepare_to_wait_event(&ctx->wait, &w.w, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
if (!ret2 && !t.task)
ret2 = -ETIME;
if (aio_read_events(ctx, min_nr, nr, event, &ret) || ret2)
break;
if (nr_got == ret)
schedule(); //关键在这里
}
finish_wait(&ctx->wait, &w.w);
hrtimer_cancel(&t.timer);
destroy_hrtimer_on_stack(&t.timer);
return ret;
}
在等待的时候去调用了schedule,还不如非阻塞+epoll。
特殊的文件系统/proc
在/proc目录下可以查看和修改很多内核的配置,几乎每个子系统都有对应的文件。不过/proc并不是一个普通的文件系统。
以cpuinfo为例,每个子系统都会实现一个对应的加载项fs_initcall。对文件的读写操作会被映射到对应的具体接口上去。
fs\proc\cpuinfo.c
extern const struct seq_operations cpuinfo_op;
static int cpuinfo_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
return seq_open(file, &cpuinfo_op);
}
static const struct proc_ops cpuinfo_proc_ops = {
.proc_flags = PROC_ENTRY_PERMANENT,
.proc_open = cpuinfo_open,
.proc_read_iter = seq_read_iter,
.proc_lseek = seq_lseek,
.proc_release = seq_release,
};
static int __init proc_cpuinfo_init(void)
{
proc_create("cpuinfo", 0, NULL, &cpuinfo_proc_ops);
return 0;
}
fs_initcall(proc_cpuinfo_init);
微信扫描下方的二维码阅读本文

0 Comments