硬件部分
- CPU上电初始化后,调用主板EEPROM芯片里的BIOS程序
BIOS = Basic Input Output System。 - BIOS程序检查完各种硬件状态后,将控制权交给主引导程序(Bootloader)
从MBR里(Master Boot Record,第1个磁盘的第1个分区)加载程序到内存中执行。
主引导程序grub2支持包括Linux在内的多种操作系统,被广泛使用。
主引导程序grub2
GRUB(GRand Unified Bootloader),grub2是第二个优化版本。
- grub2
grub2在MBR中的程序很小,启动后先挂载根分区,然后去/boot下面读取配置文件/boot/grub2/grub.cfg,加载内核并且转交控制。
set root='hd0,msdos1'
if [ x$feature_platform_search_hint = xy ]; then
search --no-floppy --fs-uuid --set=root --hint='hd0,msdos1' c8b5b2da-5565-4dc1-b002-2a8b07573e22
else
search --no-floppy --fs-uuid --set=root c8b5b2da-5565-4dc1-b002-2a8b07573e22
fi
linux16 /boot/vmlinuz-3.10.0-1160.119.1.el7.x86_64 root=UUID=c8b5b2da-5565-4dc1-b002-2a8b07573e22 ro crashkernel=auto spectre_v2=retpoline rhgb quiet net.ifnames=0 console=tty0 console=ttyS0,115200n8 noibrs nvme_core.io_timeout=4294967295 nvme_core.admin_timeout=4294967295
initrd16 /boot/initramfs-3.10.0-1160.119.1.el7.x86_64.img
上面是配置里最重要的几行,告诉grub2去设备hd0,msdos1下面找内核镜像文件/boot/vmlinuz-3.10.0-1160.119.1.el7.x86_64和/boot/initramfs-3.10.0-1160.119.1.el7.x86_64.img加载。
- initramfs
早期的内核镜像只有一个文件。因为这个阶段内核还没初始化,临时根文件系统处理起来比较复杂,所以从Kernel 1.3.73开始分离成为一个initramfs(Initial RAM File System)文件。这个文件在编译内核时通过脚本usr\gen_initramfs.sh生成。在内核加载时合并,合并的汇编代码在usr\initramfs_data.S
.section .init.ramfs,"a"
__irf_start:
.incbin "usr/initramfs_inc_data"
__irf_end:
.section .init.ramfs.info,"a"
.globl __initramfs_size
__initramfs_size:
#ifdef CONFIG_64BIT
.quad __irf_end - __irf_start
#else
.long __irf_end - __irf_start
#endif
x86内核加载协议
内核在x86架构下的启动协议参见https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/arch/x86/boot.html
内核镜像文件会打包成下面几种格式:
- vmlinux
原始的内核镜像 - zImage
vmlinux的zip压缩包 - bzImage
大内核的zip压缩包,现在发行版一般是这种,zImage已经很少使用。 - vmlinuz
vmlinux的压缩包,包括setup.elf(内核引导) + setup.bin(内核加载时硬件信息采集) + vmlinux(内核本身)
内核在实模式(Real-Mode)下前64k的内存布局如下
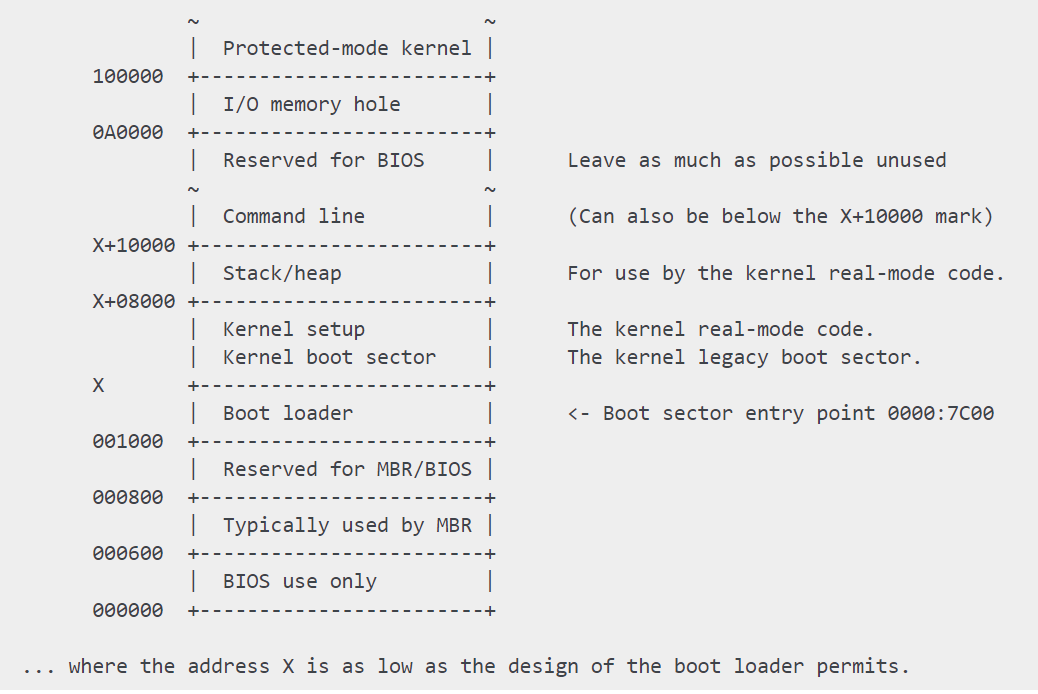
- [0x1000,0x7C00]是主引导程序grub2的地址空间
- [0x7C00,0x10000]是CPU实模式下的引导程序setup.elf
Kernel boot sector,setup.elf就在vmlinux的头部 - 0x100000开始是vmlinux
进入保护模式后直接跳到0x100000(ljmpl opcode那一行),也就是vmlinux内核的功能入口。
x86内核加载过程
架构相关的代码因为同时涉及到汇编和C,找起来会有点绕。要多从编译文件里找线索arch\x86\boot\Makefile
- setup.elf引导程序
setup.elf引导程序的入口代码在arch\x86\boot\header.S,会在内存[0x08000,0x10000]初始化一个堆栈,然后调用arch\x86\boot\main.c,进入保护模式。go_to_protected_mode的代码在arch\x86\boot\pmjump.S。
/*
* void protected_mode_jump(u32 entrypoint, u32 bootparams);
*/
SYM_FUNC_START_NOALIGN(protected_mode_jump)
movl %edx, %esi # Pointer to boot_params table
xorl %ebx, %ebx
movw %cs, %bx
shll $4, %ebx
addl %ebx, 2f
jmp 1f # Short jump to serialize on 386/486
1:
movw $__BOOT_DS, %cx
movw $__BOOT_TSS, %di
movl %cr0, %edx
orb $X86_CR0_PE, %dl # Protected mode
movl %edx, %cr0
# Transition to 32-bit mode
.byte 0x66, 0xea # ljmpl opcode
2: .long .Lin_pm32 # offset
.word __BOOT_CS # segment
SYM_FUNC_END(protected_mode_jump)
- 内核初始化(架构相关部分)
vmlinux在CPU保护模式下加载,入口在arch/x86/kernel/head_32.S(现在一般使用压缩的镜像vmlinuz,入口在arch\x86\boot\compressed\head_32.S,会先解压再跳到vmlinux)。经过一系列寄存器初始化后调用i386_start_kernel,代码在arch\x86\kernel\head32.c。
asmlinkage __visible void __init __noreturn i386_start_kernel(void)
{
/* Make sure IDT is set up before any exception happens */
idt_setup_early_handler();
load_ucode_bsp();
zap_early_initrd_mapping();
cr4_init_shadow();
sanitize_boot_params(&boot_params);
x86_early_init_platform_quirks();
/* Call the subarch specific early setup function */
switch (boot_params.hdr.hardware_subarch) {
case X86_SUBARCH_INTEL_MID:
x86_intel_mid_early_setup();
break;
case X86_SUBARCH_CE4100:
x86_ce4100_early_setup();
break;
default:
i386_default_early_setup();
break;
}
start_kernel();
}
这个函数最后调用start_kernel。
内核初始化start_kernel
start_kernel在init\main.c,从这里开始就是体系无关的内核初始化了。
几个关键模块的初始化顺序:
- 内存初始化mm_core_init
- 调度初始化sched_init
- 硬件中断初始化init_IRQ
- 控制台初始化console_init
- 网络协议栈初始化net_ns_init
- 信号初始化signals_init
- 软中断初始化softirq_init
- proc文件系统初始化proc_root_init
- 文件系统初始化nsfs_init
- init进程初始化rest_init
rest_init里会新建一个用户态进程去执行/sbin/init。Centos上/sbin/init是/lib/systemd/systemd的软链接,所以1号进程就是systemd。rest_init本身的主线程会一直循环执行sched模块的do_idle方法。至此,内核启动完毕。
详情见代码
asmlinkage __visible __init __no_sanitize_address __noreturn __no_stack_protector
void start_kernel(void)
{
char *command_line;
char *after_dashes;
set_task_stack_end_magic(&init_task);
smp_setup_processor_id();
debug_objects_early_init();
init_vmlinux_build_id();
cgroup_init_early();
local_irq_disable();
early_boot_irqs_disabled = true;
/*
* Interrupts are still disabled. Do necessary setups, then
* enable them.
*/
boot_cpu_init();
page_address_init();
pr_notice("%s", linux_banner);
early_security_init();
setup_arch(&command_line);
setup_boot_config();
setup_command_line(command_line);
setup_nr_cpu_ids();
setup_per_cpu_areas();
smp_prepare_boot_cpu(); /* arch-specific boot-cpu hooks */
early_numa_node_init();
boot_cpu_hotplug_init();
pr_notice("Kernel command line: %s\n", saved_command_line);
/* parameters may set static keys */
jump_label_init();
parse_early_param();
after_dashes = parse_args("Booting kernel",
static_command_line, __start___param,
__stop___param - __start___param,
-1, -1, NULL, &unknown_bootoption);
print_unknown_bootoptions();
if (!IS_ERR_OR_NULL(after_dashes))
parse_args("Setting init args", after_dashes, NULL, 0, -1, -1,
NULL, set_init_arg);
if (extra_init_args)
parse_args("Setting extra init args", extra_init_args,
NULL, 0, -1, -1, NULL, set_init_arg);
/* Architectural and non-timekeeping rng init, before allocator init */
random_init_early(command_line);
/*
* These use large bootmem allocations and must precede
* initalization of page allocator
*/
setup_log_buf(0);
vfs_caches_init_early();
sort_main_extable();
trap_init();
mm_core_init();
poking_init();
ftrace_init();
/* trace_printk can be enabled here */
early_trace_init();
/*
* Set up the scheduler prior starting any interrupts (such as the
* timer interrupt). Full topology setup happens at smp_init()
* time - but meanwhile we still have a functioning scheduler.
*/
sched_init();
if (WARN(!irqs_disabled(),
"Interrupts were enabled *very* early, fixing it\n"))
local_irq_disable();
radix_tree_init();
maple_tree_init();
/*
* Set up housekeeping before setting up workqueues to allow the unbound
* workqueue to take non-housekeeping into account.
*/
housekeeping_init();
/*
* Allow workqueue creation and work item queueing/cancelling
* early. Work item execution depends on kthreads and starts after
* workqueue_init().
*/
workqueue_init_early();
rcu_init();
/* Trace events are available after this */
trace_init();
if (initcall_debug)
initcall_debug_enable();
context_tracking_init();
/* init some links before init_ISA_irqs() */
early_irq_init();
init_IRQ();
tick_init();
rcu_init_nohz();
init_timers();
srcu_init();
hrtimers_init();
softirq_init();
timekeeping_init();
time_init();
/* This must be after timekeeping is initialized */
random_init();
/* These make use of the fully initialized rng */
kfence_init();
boot_init_stack_canary();
perf_event_init();
profile_init();
call_function_init();
WARN(!irqs_disabled(), "Interrupts were enabled early\n");
early_boot_irqs_disabled = false;
local_irq_enable();
kmem_cache_init_late();
/*
* HACK ALERT! This is early. We're enabling the console before
* we've done PCI setups etc, and console_init() must be aware of
* this. But we do want output early, in case something goes wrong.
*/
console_init();
if (panic_later)
panic("Too many boot %s vars at `%s'", panic_later,
panic_param);
lockdep_init();
/*
* Need to run this when irqs are enabled, because it wants
* to self-test [hard/soft]-irqs on/off lock inversion bugs
* too:
*/
locking_selftest();
#ifdef CONFIG_BLK_DEV_INITRD
if (initrd_start && !initrd_below_start_ok &&
page_to_pfn(virt_to_page((void *)initrd_start)) < min_low_pfn) {
pr_crit("initrd overwritten (0x%08lx < 0x%08lx) - disabling it.\n",
page_to_pfn(virt_to_page((void *)initrd_start)),
min_low_pfn);
initrd_start = 0;
}
#endif
setup_per_cpu_pageset();
numa_policy_init();
acpi_early_init();
if (late_time_init)
late_time_init();
sched_clock_init();
calibrate_delay();
arch_cpu_finalize_init();
pid_idr_init();
anon_vma_init();
#ifdef CONFIG_X86
if (efi_enabled(EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES))
efi_enter_virtual_mode();
#endif
thread_stack_cache_init();
cred_init();
fork_init();
proc_caches_init();
uts_ns_init();
key_init();
security_init();
dbg_late_init();
net_ns_init();
vfs_caches_init();
pagecache_init();
signals_init();
seq_file_init();
proc_root_init();
nsfs_init();
pidfs_init();
cpuset_init();
cgroup_init();
taskstats_init_early();
delayacct_init();
acpi_subsystem_init();
arch_post_acpi_subsys_init();
kcsan_init();
/* Do the rest non-__init'ed, we're now alive */
rest_init();
/*
* Avoid stack canaries in callers of boot_init_stack_canary for gcc-10
* and older.
*/
#if !__has_attribute(__no_stack_protector__)
prevent_tail_call_optimization();
#endif
}
微信扫描下方的二维码阅读本文

0 Comments