前言
HDFS已经解决了海量数据的存储问题。MapReduce框架则是用来解决基于HDFS存储的分布式计算问题。
MapReduce编程API
public interface Mapper<K1, V1, K2, V2> extends JobConfigurable, Closeable {
void map(K1 key, V1 value, OutputCollector<K2, V2> output, Reporter reporter)
throws IOException;
}
public interface Reducer<K2, V2, K3, V3> extends JobConfigurable, Closeable {
void reduce(K2 key, Iterator<V2> values,
OutputCollector<K3, V3> output, Reporter reporter)
throws IOException;
}
Mapper接口可以简单理解为扫描文件的逻辑,Reducer接口为合并Mapper结果的逻辑。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "word count");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
根据业务逻辑写好Mapper和Reducer的实现,设置好输入输出源,打包成jar包后,就可以交给Yarn去调度执行了。
yarn classpath [--glob |--jar <path> |-h |--help]
Yarn会将程序打包上传到HDFS,本地计算后将结果返回给客户端。
MapReduce任务执行
提交Job到Cluster的源代码在这里
hadoop\hadoop-mapreduce-project\hadoop-mapreduce-client\hadoop-mapreduce-client-core\src\main\java\org\apache\hadoop\mapreduce\JobSubmitter.java
Job有两种执行方式:本地执行和Yarn执行。
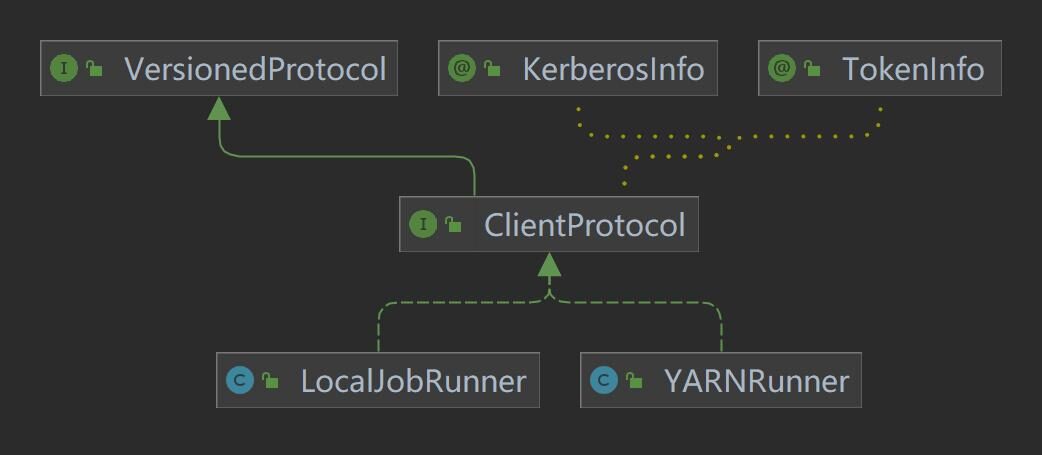
Job本地启动代码在这里
hadoop\hadoop-mapreduce-project\hadoop-mapreduce-client\hadoop-mapreduce-client-common\src\main\java\org\apache\hadoop\mapred\LocalJobRunner.java
public void run() {
JobID jobId = profile.getJobID();
JobContext jContext = new JobContextImpl(job, jobId);
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.OutputCommitter outputCommitter = null;
try {
outputCommitter = createOutputCommitter(conf.getUseNewMapper(), jobId, conf);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.info("Failed to createOutputCommitter", e);
return;
}
try {
TaskSplitMetaInfo[] taskSplitMetaInfos =
SplitMetaInfoReader.readSplitMetaInfo(jobId, localFs, conf, systemJobDir);
int numReduceTasks = job.getNumReduceTasks();
outputCommitter.setupJob(jContext);
status.setSetupProgress(1.0f);
Map<TaskAttemptID, MapOutputFile> mapOutputFiles =
Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<TaskAttemptID, MapOutputFile>());
List<RunnableWithThrowable> mapRunnables = getMapTaskRunnables(
taskSplitMetaInfos, jobId, mapOutputFiles);
initCounters(mapRunnables.size(), numReduceTasks);
ExecutorService mapService = createMapExecutor();
runTasks(mapRunnables, mapService, "map");
try {
if (numReduceTasks > 0) {
List<RunnableWithThrowable> reduceRunnables = getReduceTaskRunnables(
jobId, mapOutputFiles);
ExecutorService reduceService = createReduceExecutor();
runTasks(reduceRunnables, reduceService, "reduce");
}
} finally {
for (MapOutputFile output : mapOutputFiles.values()) {
output.removeAll();
}
}
// delete the temporary directory in output directory
outputCommitter.commitJob(jContext);
status.setCleanupProgress(1.0f);
if (killed) {
this.status.setRunState(JobStatus.KILLED);
} else {
this.status.setRunState(JobStatus.SUCCEEDED);
}
JobEndNotifier.localRunnerNotification(job, status);
} catch (Throwable t) {
try {
outputCommitter.abortJob(jContext,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobStatus.State.FAILED);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
LOG.info("Error cleaning up job:" + id);
}
status.setCleanupProgress(1.0f);
if (killed) {
this.status.setRunState(JobStatus.KILLED);
} else {
this.status.setRunState(JobStatus.FAILED);
}
LOG.warn(id.toString(), t);
JobEndNotifier.localRunnerNotification(job, status);
} finally {
try {
try {
// Cleanup distributed cache
localDistributedCacheManager.close();
} finally {
try {
fs.delete(systemJobFile.getParent(), true); // delete submit dir
} finally {
localFs.delete(localJobFile, true); // delete local copy
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.warn("Error cleaning up "+id+": "+e);
}
}
}
下图是MapReduce的执行过程
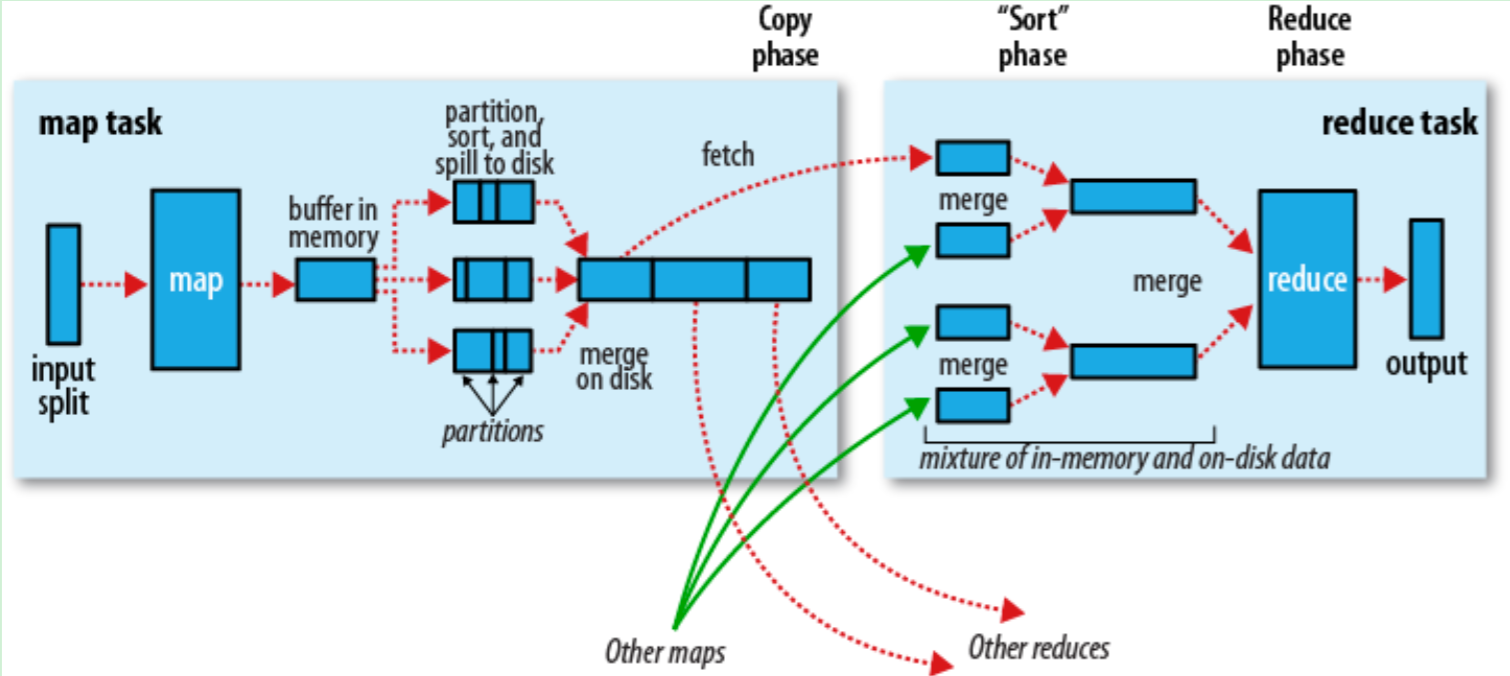
MapReduce这套API虽然可用,但是有两个致命的缺陷:
- 编织工作流的方式太过原始,写业务逻辑非常繁琐
- 每一步计算都需要把数据写到HDFS文件又重新加载回内存,性能损失严重
现在已经基本很少直接在这一层写代码了。Hive改进了第一条,Spark改进了上面两条,这个后面会继续深入学习。
Yarn集群启动下一篇文章继续。
微信扫描下方的二维码阅读本文

0 Comments