一直到Java8之前,面向对象都是Java的唯一圣经,那就从类开始学习。
class文件结构
每个.java文件经过javac编程后,都会得到一个.class文件。.jar就是一堆.class文件的zip压缩包。
在虚拟机眼中的类就是.class文件,它的结构如下:
#src/jdk.jdeps/share/classes/com/sun/tools/classfile/ClassFile.java
public class ClassFile {
public final int magic;
public final int minor_version;
public final int major_version;
public final ConstantPool constant_pool;
public final AccessFlags access_flags;
public final int this_class;
public final int super_class;
public final int[] interfaces;
public final Field[] fields;
public final Method[] methods;
public final Attributes attributes;
}
版本,常量池,访问标记,类,父类,接口,字段,方法,属性。看起来没什么特别的,和Python的类差不多,就多了接口的概念。顺便说一句,Python也有JVM的实现,Jython完全符合CPython标准,但是项目一直不温不火。
当然上面是在Java层的定义,在C++层的定义在src\hotspot\share\classfile\classFileParser.hpp
下图是用IEDA插件jclasslib查看到的HashMap.class
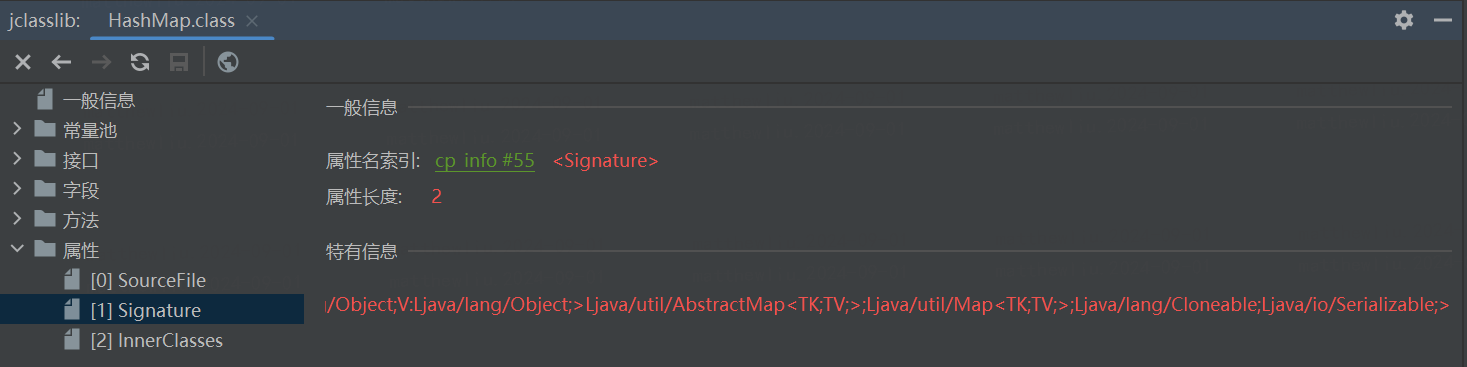
注意签名里是没有范型信息的,有的只是TK、TV占位符。这就Java的范型类型檫除机制,避免虚拟机里有大量的HashMap类实例。不过也可以通过代码层面强制虚拟机创建HashMap的实例。
比如Spring中的ParameterizedTypeReference
ParameterizedTypeReference<GraphqlApplication> typeReference = new ParameterizedTypeReference<GraphqlApplication>() {
};
这里每次创建的内部类都会把范型的类型带到签名里去,所以有机会在运行期拿到范型的实际类型GraphqlApplication。
class文件解析
.class文件的解析过程在src\hotspot\share\classfile\classFileParser.cpp#ClassFileParser::parse_stream
这个parse_stream函数,就是解析二进制文件的过程,感兴趣的可以细看一下。
class文件加载
加载过程在KlassFactory类上。最终每个class文件会生成一个C++层的InstanceKlass对象,保存了Java类在运行期的所有必要信息。
src\hotspot\share\classfile\klassFactory.cpp
// called during initial loading of a shared class
InstanceKlass* KlassFactory::check_shared_class_file_load_hook(
InstanceKlass* ik,
Symbol* class_name,
Handle class_loader,
Handle protection_domain, TRAPS) {
#if INCLUDE_CDS && INCLUDE_JVMTI
assert(ik != NULL, "sanity");
assert(ik->is_shared(), "expecting a shared class");
if (JvmtiExport::should_post_class_file_load_hook()) {
assert(THREAD->is_Java_thread(), "must be JavaThread");
// Post the CFLH
JvmtiCachedClassFileData* cached_class_file = NULL;
JvmtiCachedClassFileData* archived_class_data = ik->get_archived_class_data();
assert(archived_class_data != NULL, "shared class has no archived class data");
unsigned char* ptr =
VM_RedefineClasses::get_cached_class_file_bytes(archived_class_data);
unsigned char* end_ptr =
ptr + VM_RedefineClasses::get_cached_class_file_len(archived_class_data);
unsigned char* old_ptr = ptr;
JvmtiExport::post_class_file_load_hook(class_name,
class_loader,
protection_domain,
&ptr,
&end_ptr,
&cached_class_file);
if (old_ptr != ptr) {
// JVMTI agent has modified class file data.
// Set new class file stream using JVMTI agent modified class file data.
ClassLoaderData* loader_data =
ClassLoaderData::class_loader_data(class_loader());
int path_index = ik->shared_classpath_index();
const char* pathname;
if (path_index < 0) {
// shared classes loaded by user defined class loader
// do not have shared_classpath_index
ModuleEntry* mod_entry = ik->module();
if (mod_entry != NULL && (mod_entry->location() != NULL)) {
ResourceMark rm;
pathname = (const char*)(mod_entry->location()->as_C_string());
} else {
pathname = "";
}
} else {
SharedClassPathEntry* ent =
(SharedClassPathEntry*)FileMapInfo::shared_path(path_index);
pathname = ent == NULL ? NULL : ent->name();
}
ClassFileStream* stream = new ClassFileStream(ptr,
end_ptr - ptr,
pathname,
ClassFileStream::verify);
ClassFileParser parser(stream,
class_name,
loader_data,
protection_domain,
NULL,
NULL,
ClassFileParser::BROADCAST, // publicity level
CHECK_NULL);
InstanceKlass* new_ik = parser.create_instance_klass(true /* changed_by_loadhook */,
CHECK_NULL);
if (cached_class_file != NULL) {
new_ik->set_cached_class_file(cached_class_file);
}
if (class_loader.is_null()) {
ResourceMark rm;
ClassLoader::add_package(class_name->as_C_string(), path_index, THREAD);
}
return new_ik;
}
}
#endif
return NULL;
}
微信扫描下方的二维码阅读本文

0 Comments