白皮书
比特币白皮书在这里https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
各种语言的版本都有。
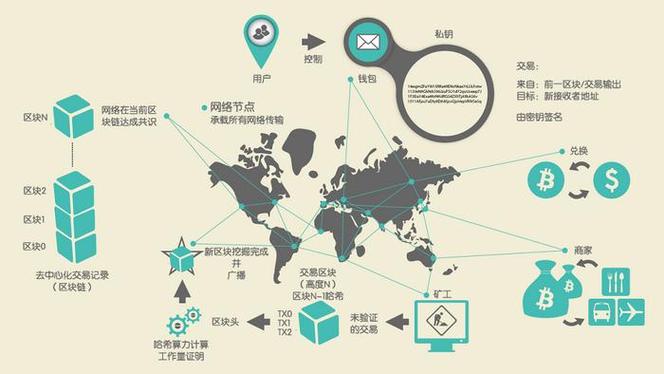
本文只关注源代码,尽量讲清楚而又不掉入细节中。
类图结构
BTC程序大致结构图如下
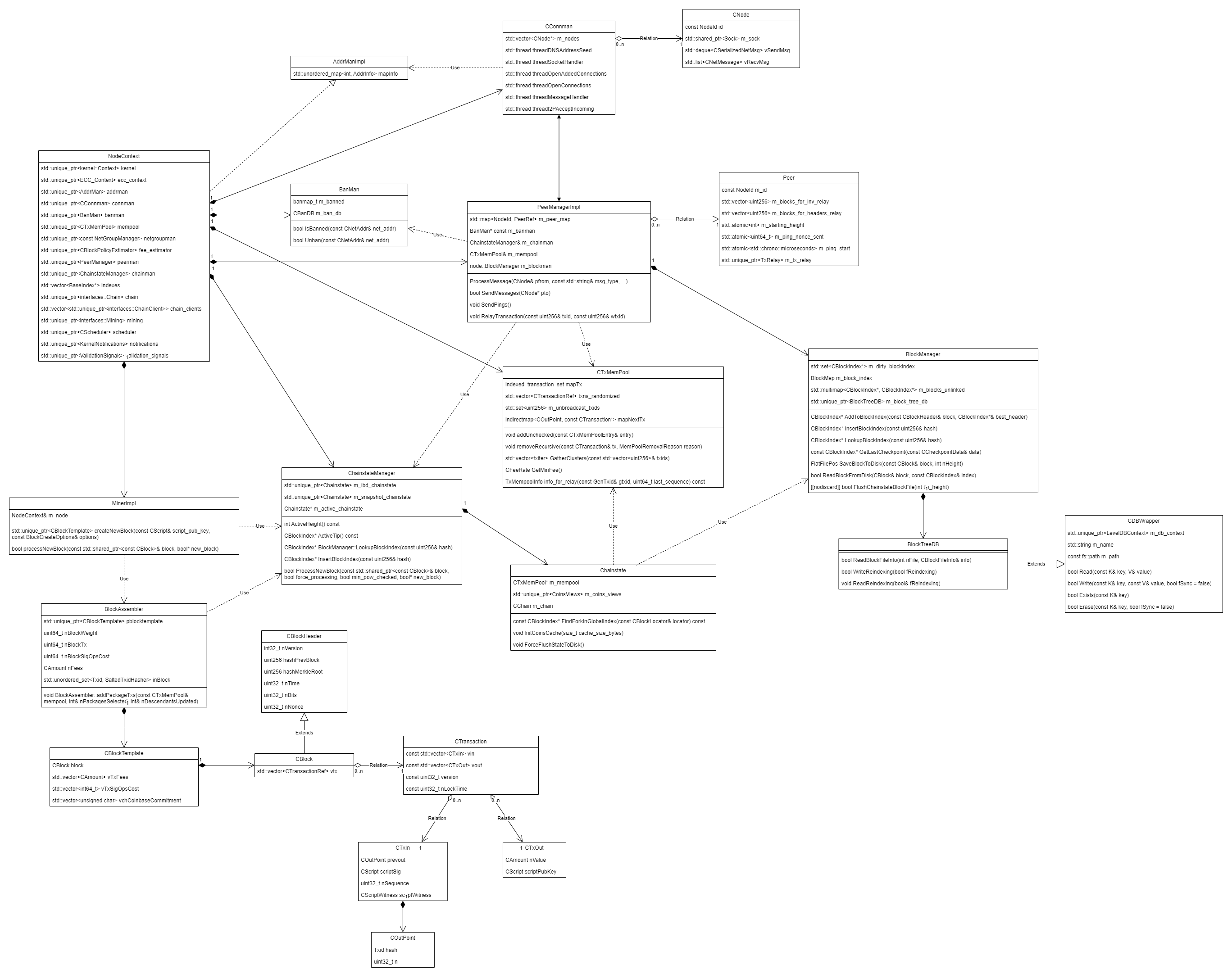
- 全局接口类NodeContext
模块间的调用都通过这个全局的接口类转接,简化代码依赖 - 节点管理对象PeerManagerImpl
- 区块管理BlockManager
- 内存中当前块和事务CTxMemPool
- 挖矿MinerImpl
打包BlockAssembler - 区块结构CBlock
- 交易结构CTransaction
启动节点
启动节点的代码在src\bitcoind.cpp
static bool AppInit(NodeContext& node)
{
...
// Lock data directory after daemonization
if (!AppInitLockDataDirectory())
{
// If locking the data directory failed, exit immediately
return false;
}
fRet = AppInitInterfaces(node) && AppInitMain(node);
...
}
核心函数是AppInitMain
- 初始化进程
- 独占锁定data目录
- 设置周期性任务
- 每分钟变更随机数种子
- 每5分钟检查磁盘空间是否大于50 MB
- 处理钱包
-wallet - 初始化各种RPC Handler
- 初始化网络
-listen、-discover、-asmap、-proxy - 加载链
LoadChainstate、VerifyLoadedChainstate - 是否需要处理索引
-txindex,裁剪PruneAndFlush - 加载区块
ImportBlocks - 启动节点
-seednode、-connect - 启动各种RPC
消息类型
消息定义在src\protocol.h
/** All known message types (see above). Keep this in the same order as the list of messages above. */
inline const std::array ALL_NET_MESSAGE_TYPES{std::to_array<std::string>({
NetMsgType::VERSION,
NetMsgType::VERACK,
NetMsgType::ADDR,
NetMsgType::ADDRV2,
NetMsgType::SENDADDRV2,
NetMsgType::INV,
NetMsgType::GETDATA,
NetMsgType::MERKLEBLOCK,
NetMsgType::GETBLOCKS,
NetMsgType::GETHEADERS,
NetMsgType::TX,
NetMsgType::HEADERS,
NetMsgType::BLOCK,
NetMsgType::GETADDR,
NetMsgType::MEMPOOL,
NetMsgType::PING,
NetMsgType::PONG,
NetMsgType::NOTFOUND,
NetMsgType::FILTERLOAD,
NetMsgType::FILTERADD,
NetMsgType::FILTERCLEAR,
NetMsgType::SENDHEADERS,
NetMsgType::FEEFILTER,
NetMsgType::SENDCMPCT,
NetMsgType::CMPCTBLOCK,
NetMsgType::GETBLOCKTXN,
NetMsgType::BLOCKTXN,
NetMsgType::GETCFILTERS,
NetMsgType::CFILTER,
NetMsgType::GETCFHEADERS,
NetMsgType::CFHEADERS,
NetMsgType::GETCFCHECKPT,
NetMsgType::CFCHECKPT,
NetMsgType::WTXIDRELAY,
NetMsgType::SENDTXRCNCL,
})};
消息处理代码在这里src\net_processing.cpp
void PeerManagerImpl::ProcessMessage(CNode& pfrom, const std::string& msg_type, DataStream& vRecv,
const std::chrono::microseconds time_received,
const std::atomic<bool>& interruptMsgProc)
{
省略
if (msg_type == NetMsgType::VERSION) {
省略
}
if (msg_type == NetMsgType::VERACK) {
省略
}
}
整个函数就是这样的几十个if处理消息。几个基本消息:
- 节点握手
VERSION、VERACK、PING、PONG - 查询节点地址
GETADDR、ADDR、SENDADDRV2、ADDRV2 - 区块
HEADERS、GETHEADERS、INV、GETBLOCKS、GETDATA、BLOCK - 交易
TX、BLOCKTXN
交易和区块
- 交易结构
交易结构代码CTransaction在代码src\primitives\transaction.h
class COutPoint
{
public:
Txid hash; //前置交易Hash
uint32_t n; //前置交易序号
}
class CTxIn
{
public:
COutPoint prevout;
CScript scriptSig; //交易发起方的签名
uint32_t nSequence; //本次交易序号
CScriptWitness scriptWitness; //!< Only serialized through CTransaction
}
class CTxOut
{
public:
CAmount nValue; //本次交易的数值
CScript scriptPubKey; //交易目标方解锁脚本
}
class CTransaction
{
public:
// The local variables are made const to prevent unintended modification
// without updating the cached hash value. However, CTransaction is not
// actually immutable; deserialization and assignment are implemented,
// and bypass the constness. This is safe, as they update the entire
// structure, including the hash.
const std::vector<CTxIn> vin;
const std::vector<CTxOut> vout;
const uint32_t version;
const uint32_t nLockTime;
}
- 区块结构
区块结构CBlock,区块头定义在src\primitives\block.h
class CBlockHeader{
public:
// header
int32_t nVersion; //版本
uint256 hashPrevBlock; // 上一个区块的hash值
uint256 hashMerkleRoot; // 本区块Merkle根hash值
uint32_t nTime; //时间
uint32_t nBits; // 难度控制
uint32_t nNonce; // 随机数
}
class CBlock : public CBlockHeader{
public:
std::vector<CTransactionRef> vtx; // 本区块的交易
}
以上区块和交易信息可以通过命令查看到详情bitcoin-cli getblock <blockhash>
打包和挖矿
普通节点不需要打包和挖矿,跟随其他节点,负责接收和广播交易就可以了。只有专门的矿工节点才需要处理打包和挖矿。
- 创建交易
命令行工具代码在src\rpc\rawtransaction.cpp
节点接收交易的代码在src\validation.cpp
MempoolAcceptResult AcceptToMemoryPool(Chainstate& active_chainstate, const CTransactionRef& tx,
int64_t accept_time, bool bypass_limits, bool test_accept)
{
AssertLockHeld(::cs_main);
const CChainParams& chainparams{active_chainstate.m_chainman.GetParams()};
assert(active_chainstate.GetMempool() != nullptr);
CTxMemPool& pool{*active_chainstate.GetMempool()};
std::vector<COutPoint> coins_to_uncache;
auto args = MemPoolAccept::ATMPArgs::SingleAccept(chainparams, accept_time, bypass_limits, coins_to_uncache, test_accept);
MempoolAcceptResult result = MemPoolAccept(pool, active_chainstate).AcceptSingleTransaction(tx, args);
if (result.m_result_type != MempoolAcceptResult::ResultType::VALID) {
// Remove coins that were not present in the coins cache before calling
// AcceptSingleTransaction(); this is to prevent memory DoS in case we receive a large
// number of invalid transactions that attempt to overrun the in-memory coins cache
// (`CCoinsViewCache::cacheCoins`).
for (const COutPoint& hashTx : coins_to_uncache)
active_chainstate.CoinsTip().Uncache(hashTx);
TRACE2(mempool, rejected,
tx->GetHash().data(),
result.m_state.GetRejectReason().c_str()
);
}
// After we've (potentially) uncached entries, ensure our coins cache is still within its size limits
BlockValidationState state_dummy;
active_chainstate.FlushStateToDisk(state_dummy, FlushStateMode::PERIODIC);
return result;
}
- 打包
打包交易的代码在src\node\miner.cpp
std::unique_ptr<CBlockTemplate> BlockAssembler::CreateNewBlock(const CScript& scriptPubKeyIn)
{
const auto time_start{SteadyClock::now()};
resetBlock();
pblocktemplate.reset(new CBlockTemplate());
if (!pblocktemplate.get()) {
return nullptr;
}
CBlock* const pblock = &pblocktemplate->block; // pointer for convenience
// Add dummy coinbase tx as first transaction
pblock->vtx.emplace_back();
pblocktemplate->vTxFees.push_back(-1); // updated at end
pblocktemplate->vTxSigOpsCost.push_back(-1); // updated at end
LOCK(::cs_main);
CBlockIndex* pindexPrev = m_chainstate.m_chain.Tip();
assert(pindexPrev != nullptr);
nHeight = pindexPrev->nHeight + 1;
pblock->nVersion = m_chainstate.m_chainman.m_versionbitscache.ComputeBlockVersion(pindexPrev, chainparams.GetConsensus());
// -regtest only: allow overriding block.nVersion with
// -blockversion=N to test forking scenarios
if (chainparams.MineBlocksOnDemand()) {
pblock->nVersion = gArgs.GetIntArg("-blockversion", pblock->nVersion);
}
pblock->nTime = TicksSinceEpoch<std::chrono::seconds>(NodeClock::now());
m_lock_time_cutoff = pindexPrev->GetMedianTimePast();
int nPackagesSelected = 0;
int nDescendantsUpdated = 0;
if (m_mempool) {
LOCK(m_mempool->cs);
addPackageTxs(*m_mempool, nPackagesSelected, nDescendantsUpdated);
}
const auto time_1{SteadyClock::now()};
m_last_block_num_txs = nBlockTx;
m_last_block_weight = nBlockWeight;
// Create coinbase transaction.
CMutableTransaction coinbaseTx;
coinbaseTx.vin.resize(1);
coinbaseTx.vin[0].prevout.SetNull();
coinbaseTx.vout.resize(1);
coinbaseTx.vout[0].scriptPubKey = scriptPubKeyIn;
coinbaseTx.vout[0].nValue = nFees + GetBlockSubsidy(nHeight, chainparams.GetConsensus());
coinbaseTx.vin[0].scriptSig = CScript() << nHeight << OP_0;
pblock->vtx[0] = MakeTransactionRef(std::move(coinbaseTx));
pblocktemplate->vchCoinbaseCommitment = m_chainstate.m_chainman.GenerateCoinbaseCommitment(*pblock, pindexPrev);
pblocktemplate->vTxFees[0] = -nFees;
LogPrintf("CreateNewBlock(): block weight: %u txs: %u fees: %ld sigops %d\n", GetBlockWeight(*pblock), nBlockTx, nFees, nBlockSigOpsCost);
// Fill in header
pblock->hashPrevBlock = pindexPrev->GetBlockHash();
UpdateTime(pblock, chainparams.GetConsensus(), pindexPrev);
pblock->nBits = GetNextWorkRequired(pindexPrev, pblock, chainparams.GetConsensus());
pblock->nNonce = 0;
pblocktemplate->vTxSigOpsCost[0] = WITNESS_SCALE_FACTOR * GetLegacySigOpCount(*pblock->vtx[0]);
BlockValidationState state;
if (m_options.test_block_validity && !TestBlockValidity(state, chainparams, m_chainstate, *pblock, pindexPrev,
/*fCheckPOW=*/false, /*fCheckMerkleRoot=*/false)) {
throw std::runtime_error(strprintf("%s: TestBlockValidity failed: %s", __func__, state.ToString()));
}
const auto time_2{SteadyClock::now()};
LogDebug(BCLog::BENCH, "CreateNewBlock() packages: %.2fms (%d packages, %d updated descendants), validity: %.2fms (total %.2fms)\n",
Ticks<MillisecondsDouble>(time_1 - time_start), nPackagesSelected, nDescendantsUpdated,
Ticks<MillisecondsDouble>(time_2 - time_1),
Ticks<MillisecondsDouble>(time_2 - time_start));
return std::move(pblocktemplate);
}
- 计算挖矿奖励
所有的比特比起始于挖矿奖励,也叫做Coinbase。每过4年奖励减半。
CAmount GetBlockSubsidy(int nHeight, const Consensus::Params& consensusParams)
{
int halvings = nHeight / consensusParams.nSubsidyHalvingInterval;
// Force block reward to zero when right shift is undefined.
if (halvings >= 64)
return 0;
CAmount nSubsidy = 50 * COIN;
// Subsidy is cut in half every 210,000 blocks which will occur approximately every 4 years.
nSubsidy >>= halvings;
return nSubsidy;
}
- 挖矿工作量证明
static bool GenerateBlock(ChainstateManager& chainman, Mining& miner, CBlock& block, uint64_t& max_tries, std::shared_ptr<const CBlock>& block_out, bool process_new_block)
{
block_out.reset();
block.hashMerkleRoot = BlockMerkleRoot(block);
while (max_tries > 0 && block.nNonce < std::numeric_limits<uint32_t>::max() && !CheckProofOfWork(block.GetHash(), block.nBits, chainman.GetConsensus()) && !chainman.m_interrupt) {
++block.nNonce;
--max_tries;
}
if (max_tries == 0 || chainman.m_interrupt) {
return false;
}
if (block.nNonce == std::numeric_limits<uint32_t>::max()) {
return true;
}
block_out = std::make_shared<const CBlock>(block);
if (!process_new_block) return true;
if (!miner.processNewBlock(block_out, nullptr)) {
throw JSONRPCError(RPC_INTERNAL_ERROR, "ProcessNewBlock, block not accepted");
}
return true;
}
通过从0开始尝试block.nNonce值,来满足nBits的难度要求。
- 广播区块
将区块写入本地链,然后通过HEADERS命令将区块广播出去。
注意:
现在都是专用矿机挖矿了,CPU挖矿代码只能做个参考。bitcoin-cli generatetoaddress
只有交易被打包进了区块链,才算真正完成。而且因为有最长链的竞争,一般区块高度过了6个后才比较保险,否则可能会因为暂时处于短链中,而被回退。
共识
以上都是确定性的代码,还没有涉及去中心化的内容。
和去中心化相对的是中心化(集中式),而不是分布式。去中心化和集中式都有非常优秀的分布式系统案例。
去中心化的预设前提是:网络中的任何一个节点都可能是不可信的,但是大部分的节点是可信的。不可性包括,客观的系统不稳定和主观的作弊、搞破坏等。
所以在信任和使用其他节点广播过来的信息之前,都需要经过验证和确认。
- 最长链竞争
节点会优先选择最长链来工作,最长链上有最多的工作量。
代码在src\validation.cpp
/**
* Return the tip of the chain with the most work in it, that isn't
* known to be invalid (it's however far from certain to be valid).
*/
CBlockIndex* Chainstate::FindMostWorkChain()
{
AssertLockHeld(::cs_main);
do {
CBlockIndex *pindexNew = nullptr;
// Find the best candidate header.
{
std::set<CBlockIndex*, CBlockIndexWorkComparator>::reverse_iterator it = setBlockIndexCandidates.rbegin();
if (it == setBlockIndexCandidates.rend())
return nullptr;
pindexNew = *it;
}
// Check whether all blocks on the path between the currently active chain and the candidate are valid.
// Just going until the active chain is an optimization, as we know all blocks in it are valid already.
CBlockIndex *pindexTest = pindexNew;
bool fInvalidAncestor = false;
while (pindexTest && !m_chain.Contains(pindexTest)) {
assert(pindexTest->HaveNumChainTxs() || pindexTest->nHeight == 0);
// Pruned nodes may have entries in setBlockIndexCandidates for
// which block files have been deleted. Remove those as candidates
// for the most work chain if we come across them; we can't switch
// to a chain unless we have all the non-active-chain parent blocks.
bool fFailedChain = pindexTest->nStatus & BLOCK_FAILED_MASK;
bool fMissingData = !(pindexTest->nStatus & BLOCK_HAVE_DATA);
if (fFailedChain || fMissingData) {
// Candidate chain is not usable (either invalid or missing data)
if (fFailedChain && (m_chainman.m_best_invalid == nullptr || pindexNew->nChainWork > m_chainman.m_best_invalid->nChainWork)) {
m_chainman.m_best_invalid = pindexNew;
}
CBlockIndex *pindexFailed = pindexNew;
// Remove the entire chain from the set.
while (pindexTest != pindexFailed) {
if (fFailedChain) {
pindexFailed->nStatus |= BLOCK_FAILED_CHILD;
m_blockman.m_dirty_blockindex.insert(pindexFailed);
} else if (fMissingData) {
// If we're missing data, then add back to m_blocks_unlinked,
// so that if the block arrives in the future we can try adding
// to setBlockIndexCandidates again.
m_blockman.m_blocks_unlinked.insert(
std::make_pair(pindexFailed->pprev, pindexFailed));
}
setBlockIndexCandidates.erase(pindexFailed);
pindexFailed = pindexFailed->pprev;
}
setBlockIndexCandidates.erase(pindexTest);
fInvalidAncestor = true;
break;
}
pindexTest = pindexTest->pprev;
}
if (!fInvalidAncestor)
return pindexNew;
} while(true);
}
- P2P网络
这部分参见Gossip协议那篇
交易脚本
交易结构中,交易输出中有个验证脚本CTxOut.scriptPubKey。内容一般如下
OP_DUP OP_HASH160 接收方公钥Hash OP_EQUALVERIFY OP_CHECKSIG
脚本含义是:谁能提供一个公钥和签名,让这个脚本校验通过,这笔交易的钱就是谁的。
所以在比特币网络,花钱就是签名,收钱就是验签。
比特币脚本的指令集是很弱的,不支持循环和跳转,指令条数也不多,无法支持复杂的金融场景。所以后来有了以太坊,他的脚本是图灵完备的。
微信扫描下方的二维码阅读本文

0 Comments